Difference between revisions of "Create Storage Pool"
m (→Encryption) |
m (→Encryption) |
||
| (34 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | == | + | == Overview == |
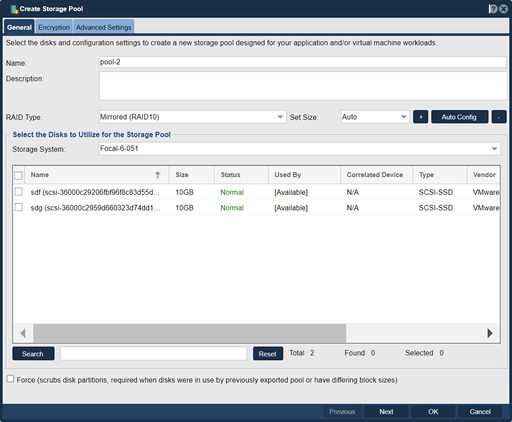
| − | [[File: | + | [[File:Crt Strg Pool - General.jpg|thumb|512px|This dialog allows you to choose disks for the Pool only from the selected Storage System.]] |
| + | In QuantaStor, the "Create Storage Pool" feature serves the purpose of creating logical storage pools that aggregate physical storage resources into a unified and manageable entity. Creation of scale-out file, block, and object Storage Pools is done in the Scale-out Storage Configuration tab and requires at least three QuantaStor systems. In contrast, scale-up Storage Pools only require a single system and can be made highly-available (HA) when two QuantaStor systems have shared access to the media via SAS or dual-ported NVMe connectivity. The primary goal of creating a storage pool is to provide a flexible and scalable storage solution that can be allocated and managed efficiently within the QuantaStor environment. | ||
| − | + | Here are some key purposes and functionalities of the "Create Storage Pool" feature in QuantaStor: | |
| + | |||
| + | *Aggregating physical storage: The feature allows you to combine multiple physical disks or storage devices into a single logical pool. This aggregation enables you to utilize the storage capacity and performance of the underlying devices in a unified manner. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Storage provisioning: By creating a storage pool, you can allocate storage capacity to different volumes or shares based on your requirements. This allows you to efficiently provision storage resources to applications, virtual machines, or users. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *RAID configuration: QuantaStor supports various RAID configurations, and the "Create Storage Pool" feature enables you to select the appropriate RAID level for your storage pool. RAID provides data redundancy and protection against disk failures. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Performance optimization: QuantaStor offers features such as caching, tiering, and striping to optimize storage performance. When creating a storage pool, you can configure these performance-enhancing options based on your workload and performance goals. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Thin provisioning: Thin provisioning allows you to allocate storage capacity dynamically as needed, rather than assigning the full capacity upfront. The "Create Storage Pool" feature enables you to enable thin provisioning for efficient utilization of storage resources. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Snapshot and cloning: QuantaStor supports snapshot and cloning functionalities, which allow you to capture point-in-time copies of your data and create clones for testing or backup purposes. When creating a storage pool, you can configure the settings for snapshot and cloning operations. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Data management and monitoring: Once a storage pool is created, QuantaStor provides a range of management and monitoring capabilities for the pool. This includes monitoring capacity usage, performance metrics, and health status of the pool. | ||
| + | |||
| + | By utilizing the "Create Storage Pool" feature in QuantaStor, you can establish logical storage entities that offer efficient allocation, protection, and management of your physical storage resources. | ||
'''Navigation:''' Storage Management --> Storage Pools --> Storage Pool --> Create (toolbar) | '''Navigation:''' Storage Management --> Storage Pools --> Storage Pool --> Create (toolbar) | ||
| − | === Selecting the RAID Type === | + | === Selecting the Storage Pool Layout (RAID Type) === |
| − | Storage pools have support for software RAID levels including | + | Storage pools have support for software RAID levels including Single-Parity, Double-Parity, Triple-Parity and Mirroring. There is also a Striped (RAID0) mode that should not be used in production but is sometimes useful for performance testing work. Scale-up Storage Pools may be expanded at any time via the Grow Storage Pool dialog and pools based on HDDs should have at least 3x SSDs added for metadata-offload and small files. |
| + | |||
| + | === Auto-Config === | ||
| + | When creating Storage Pools on large systems with many devices (eg 100+) it can be time consuming to identify which devices to select in order to achieve even selection of devices across enclosures and involves a lot of clicking which is error prone. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The automatic configuration button "Auto-Config" solves this problem. It is an intelligent device selector which will select groups of devices that are the stripe length of the selected layout. For example, if Double-Parity is selected by default devices are selected in group of 6 to facilitate creation of a pool that is using 4d+2p double parity. When the Auto-Config button is pressed the system first identifies the capacity of device that is most plentiful and uses that group to select from. Next, it tries to use half the available devices in the group to select them for the new pool. For example, if there are 10x 3.84TB SSDs and 60x 24TB HDDs the auto configurator will select 30x of the available 24TB HDDs (as this is divisible by a 4d+2p stripe) and will ignore the SSDs. (SSDs should be added to the pool after it is formed via the '''Add Log, Cache & Metadata Devices''' dialog). The other key thing that the auto-configurator does is it selects devices intelligently to achieve enclosure redundancy. Continuing the example, if the system has 3x JBODs with 20x HDDs in JBOD1, 20x HDDs in JBOD2, and 20x HDDs in JBOD3 then it would select 10x devices from each JBOD. In another example, if the system has 3x JBODs with 30x HDDs in JBOD1, 20x HDDs in JBOD2, and 10x HDDs in JBOD3 then it would still select 10x devices from each JBOD as this would achieve enclosure redundancy. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Note, it is recommended that you unselect all devices before pressing the Auto-Config button. Any devices that are already selected are ignored and the selection is preserved which can result in a selection of devices that isn't correct or enclosure redundant. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== Auto-config (+) and (-) Buttons ==== | ||
| + | The + and - buttons make it easy to add and remove a complete stripe from the pool while still following the rules of trying to achieve enclosure redundancy. Pressing the + button will add one stripe (VDEV) and pressing the - button will remove one stripe (VDEV). | ||
=== Selecting Disks === | === Selecting Disks === | ||
Storage pools typically are formed from disk drives which are multipath connected to two HBAs on two separate servers so that the pool can be made highly-available. When selecting multiple disks be sure to select disks of the same size. If one combines disks of different sizes it can compromise performance or make it less predictable. If multiple disks of differing sizes are combined together within a VDEV (group of disks) the lowest common denominator is used leaving wasted space. It is also recommended that you use disks all from the same manufacturer rather than mixing drives which may have different performance characteristics. | Storage pools typically are formed from disk drives which are multipath connected to two HBAs on two separate servers so that the pool can be made highly-available. When selecting multiple disks be sure to select disks of the same size. If one combines disks of different sizes it can compromise performance or make it less predictable. If multiple disks of differing sizes are combined together within a VDEV (group of disks) the lowest common denominator is used leaving wasted space. It is also recommended that you use disks all from the same manufacturer rather than mixing drives which may have different performance characteristics. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
==Encryption== | ==Encryption== | ||
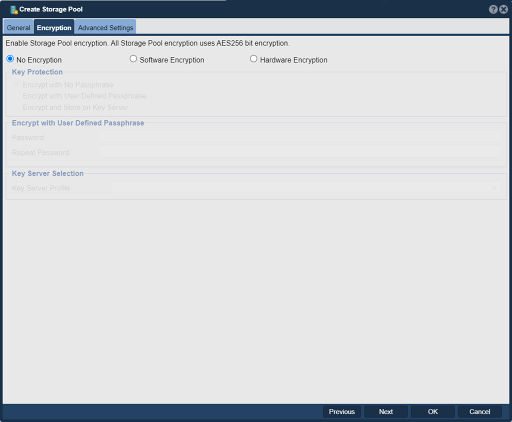
| − | [[File:Create | + | [[File:Create Strg Pool - Encrp.jpg|512px|thumb|Setup Storage Pool encryption using AES256 bit encryption.]] |
| + | === Software Encryption === | ||
| − | + | Software encryption is supported across all media types so it can be universally applied irrespective if the device is SED or not. Software Encryption is hardware accelerated via the AES-NI encryption features built into the CPU. This is supported with both Intel and AMD based CPUs and makes it such that the performance degradation due to encryption is typically limited to 15%. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | === Hardware Encryption === | |
| − | + | Hardware encryption is limited to SED SSD devices (NVMe, SATA, SAS) that are Opal 2.x or Ruby compliant. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | === Key Management via KMIP === | |
| + | |||
| + | If your organization has a KMIP server for external key management you can integrate your KMIP servers with QuantaStor by adding them in the '''Key Management Servers''' section under the '''Security''' tab. Once you've added one or more KMIP servers you'll have the option of storing the keys for your Storage Pool in your KMIP server rather than having QuantaStor store them in an encrypted file on the boot drive. | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Passphrase Protected Keys === | ||
| + | |||
| + | When creating an encrypted pool you can optionally apply a Passphrase to the pool that must be applied via the 'Start Storage Pool' dialog in order to start the pool. Pools with a user defined passphase applied will not start automatically, they require user intervention to start the pool. Applying a Passphrase to a pool is useful when transporting a system as a passphrase may be applied and then removed later. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Having a passphrase applied to a pool can complicate HA failover as in the event both systems are rebooted the passphrase must be user supplied again before the pool can start. Once the pool is started the passphrase is held encrypted in memory on both systems so that the passphrase does not need to be applied again unless both systems are rebooted at the same time. | ||
== Advanced Settings == | == Advanced Settings == | ||
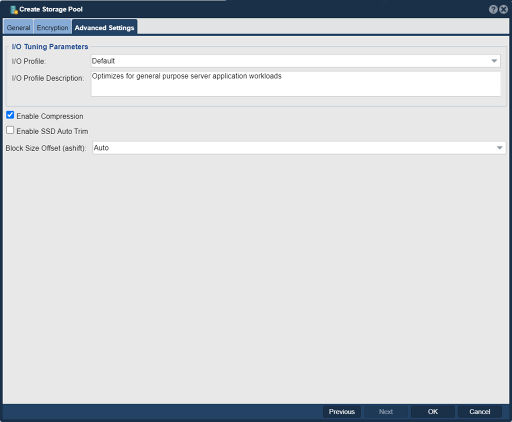
| − | [[File:Create | + | [[File:Create Strg Pool - Adv Set.jpg|512px|thumb|Setup Storage Pool I/O Tuning Parameters.]] |
Tune I/O parameters for the Storage Pool. | Tune I/O parameters for the Storage Pool. | ||
| Line 48: | Line 81: | ||
<br><br> | <br><br> | ||
| − | For additional information see [https://wiki.osnexus.com/index.php?title= | + | For additional information see [https://wiki.osnexus.com/index.php?title=Storage_Pools#Enabling_Encryption_.28One-click_Encryption.29 Admin Guide - Storage Pools] |
{{Template:ReturnToWebGuide}} | {{Template:ReturnToWebGuide}} | ||
[[Category:WebUI Dialog]] | [[Category:WebUI Dialog]] | ||
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:QuantaStor6]] |
[[Category:Requires Review]] | [[Category:Requires Review]] | ||
Latest revision as of 13:33, 20 February 2024
Contents
Overview
In QuantaStor, the "Create Storage Pool" feature serves the purpose of creating logical storage pools that aggregate physical storage resources into a unified and manageable entity. Creation of scale-out file, block, and object Storage Pools is done in the Scale-out Storage Configuration tab and requires at least three QuantaStor systems. In contrast, scale-up Storage Pools only require a single system and can be made highly-available (HA) when two QuantaStor systems have shared access to the media via SAS or dual-ported NVMe connectivity. The primary goal of creating a storage pool is to provide a flexible and scalable storage solution that can be allocated and managed efficiently within the QuantaStor environment.
Here are some key purposes and functionalities of the "Create Storage Pool" feature in QuantaStor:
- Aggregating physical storage: The feature allows you to combine multiple physical disks or storage devices into a single logical pool. This aggregation enables you to utilize the storage capacity and performance of the underlying devices in a unified manner.
- Storage provisioning: By creating a storage pool, you can allocate storage capacity to different volumes or shares based on your requirements. This allows you to efficiently provision storage resources to applications, virtual machines, or users.
- RAID configuration: QuantaStor supports various RAID configurations, and the "Create Storage Pool" feature enables you to select the appropriate RAID level for your storage pool. RAID provides data redundancy and protection against disk failures.
- Performance optimization: QuantaStor offers features such as caching, tiering, and striping to optimize storage performance. When creating a storage pool, you can configure these performance-enhancing options based on your workload and performance goals.
- Thin provisioning: Thin provisioning allows you to allocate storage capacity dynamically as needed, rather than assigning the full capacity upfront. The "Create Storage Pool" feature enables you to enable thin provisioning for efficient utilization of storage resources.
- Snapshot and cloning: QuantaStor supports snapshot and cloning functionalities, which allow you to capture point-in-time copies of your data and create clones for testing or backup purposes. When creating a storage pool, you can configure the settings for snapshot and cloning operations.
- Data management and monitoring: Once a storage pool is created, QuantaStor provides a range of management and monitoring capabilities for the pool. This includes monitoring capacity usage, performance metrics, and health status of the pool.
By utilizing the "Create Storage Pool" feature in QuantaStor, you can establish logical storage entities that offer efficient allocation, protection, and management of your physical storage resources.
Navigation: Storage Management --> Storage Pools --> Storage Pool --> Create (toolbar)
Selecting the Storage Pool Layout (RAID Type)
Storage pools have support for software RAID levels including Single-Parity, Double-Parity, Triple-Parity and Mirroring. There is also a Striped (RAID0) mode that should not be used in production but is sometimes useful for performance testing work. Scale-up Storage Pools may be expanded at any time via the Grow Storage Pool dialog and pools based on HDDs should have at least 3x SSDs added for metadata-offload and small files.
Auto-Config
When creating Storage Pools on large systems with many devices (eg 100+) it can be time consuming to identify which devices to select in order to achieve even selection of devices across enclosures and involves a lot of clicking which is error prone.
The automatic configuration button "Auto-Config" solves this problem. It is an intelligent device selector which will select groups of devices that are the stripe length of the selected layout. For example, if Double-Parity is selected by default devices are selected in group of 6 to facilitate creation of a pool that is using 4d+2p double parity. When the Auto-Config button is pressed the system first identifies the capacity of device that is most plentiful and uses that group to select from. Next, it tries to use half the available devices in the group to select them for the new pool. For example, if there are 10x 3.84TB SSDs and 60x 24TB HDDs the auto configurator will select 30x of the available 24TB HDDs (as this is divisible by a 4d+2p stripe) and will ignore the SSDs. (SSDs should be added to the pool after it is formed via the Add Log, Cache & Metadata Devices dialog). The other key thing that the auto-configurator does is it selects devices intelligently to achieve enclosure redundancy. Continuing the example, if the system has 3x JBODs with 20x HDDs in JBOD1, 20x HDDs in JBOD2, and 20x HDDs in JBOD3 then it would select 10x devices from each JBOD. In another example, if the system has 3x JBODs with 30x HDDs in JBOD1, 20x HDDs in JBOD2, and 10x HDDs in JBOD3 then it would still select 10x devices from each JBOD as this would achieve enclosure redundancy.
Note, it is recommended that you unselect all devices before pressing the Auto-Config button. Any devices that are already selected are ignored and the selection is preserved which can result in a selection of devices that isn't correct or enclosure redundant.
Auto-config (+) and (-) Buttons
The + and - buttons make it easy to add and remove a complete stripe from the pool while still following the rules of trying to achieve enclosure redundancy. Pressing the + button will add one stripe (VDEV) and pressing the - button will remove one stripe (VDEV).
Selecting Disks
Storage pools typically are formed from disk drives which are multipath connected to two HBAs on two separate servers so that the pool can be made highly-available. When selecting multiple disks be sure to select disks of the same size. If one combines disks of different sizes it can compromise performance or make it less predictable. If multiple disks of differing sizes are combined together within a VDEV (group of disks) the lowest common denominator is used leaving wasted space. It is also recommended that you use disks all from the same manufacturer rather than mixing drives which may have different performance characteristics.
Encryption
Software Encryption
Software encryption is supported across all media types so it can be universally applied irrespective if the device is SED or not. Software Encryption is hardware accelerated via the AES-NI encryption features built into the CPU. This is supported with both Intel and AMD based CPUs and makes it such that the performance degradation due to encryption is typically limited to 15%.
Hardware Encryption
Hardware encryption is limited to SED SSD devices (NVMe, SATA, SAS) that are Opal 2.x or Ruby compliant.
Key Management via KMIP
If your organization has a KMIP server for external key management you can integrate your KMIP servers with QuantaStor by adding them in the Key Management Servers section under the Security tab. Once you've added one or more KMIP servers you'll have the option of storing the keys for your Storage Pool in your KMIP server rather than having QuantaStor store them in an encrypted file on the boot drive.
Passphrase Protected Keys
When creating an encrypted pool you can optionally apply a Passphrase to the pool that must be applied via the 'Start Storage Pool' dialog in order to start the pool. Pools with a user defined passphase applied will not start automatically, they require user intervention to start the pool. Applying a Passphrase to a pool is useful when transporting a system as a passphrase may be applied and then removed later.
Having a passphrase applied to a pool can complicate HA failover as in the event both systems are rebooted the passphrase must be user supplied again before the pool can start. Once the pool is started the passphrase is held encrypted in memory on both systems so that the passphrase does not need to be applied again unless both systems are rebooted at the same time.
Advanced Settings
Tune I/O parameters for the Storage Pool.
- Default -- Optimizes for general purpose server application workloads.
- Default (SSD Optimized) -- Optimizes for pure SSD based storage pools for all workloads.
- Disk Archive -- Optimizes pool IO characteristics for disk-to-disk backup & archive applications.
- Edgeware IP TV Optimized -- Optimizes pool IO characteristics Edgeware IP TV application workflow.
- Edgeware Web TV Optimized -- Optimizes pool IO characteristics Edgeware Web TV application workflow.
- Media Post Production (Ingest Optimized) -- Optimizes pool IO characteristics for media post-production editing.
- Media Post Production (Playback Optimized) -- Optimizes pool IO characteristics for media post-production playback.
- Virtualization -- Optimizes for virtual machine workloads such as database and web servers under ESXi/XenServer/Hyper-V/Virtuozzo
For additional information see Admin Guide - Storage Pools