Difference between revisions of "Overview (Getting Started)"
m |
m (→Setup Storage Pool - Scale-out File) |
||
| (142 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | Getting Started | + | The "Getting Started" or "Configuration Guide" in QuantaStor serves as a comprehensive resource that provides instructions, recommendations, and best practices for setting up and configuring QuantaStor storage management software. |
| − | + | The purpose of the "Getting Started" or "Configuration Guide" is to assist users in the initial setup and configuration of QuantaStor. It typically covers essential topics and tasks, such as: | |
| − | + | *System Requirements: The guide outlines the hardware and software prerequisites for installing QuantaStor, including supported operating systems, storage controllers, and network configurations. | |
| + | |||
| + | *Installation Process: It provides step-by-step instructions on how to install and deploy QuantaStor on the target hardware or virtual environment. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Storage Pool Configuration: The guide explains how to create storage pools, define storage devices, and configure RAID levels or other data protection mechanisms. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Storage Volume Management: It covers the creation, modification, and deletion of storage volumes within the storage pools, including various volume types and options available. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Network Configuration: The guide may include information on configuring network interfaces, IP addresses, and network settings to enable proper connectivity and data access. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Advanced Features: It may introduce advanced features and functionalities of QuantaStor, such as replication, thin provisioning, snapshots, or high-availability configurations. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Best Practices: The guide often provides recommendations and best practices for optimizing performance, improving data reliability, and ensuring efficient management of the storage infrastructure. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The "Getting Started" or "Configuration Guide" aims to assist users in successfully setting up QuantaStor and getting their storage environment up and running. It serves as a valuable reference for understanding the various aspects of configuring and managing storage resources using QuantaStor's features and capabilities. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | '''Navigation:''' Storage Management --> Storage System --> Storage System --> Getting Started ''(toolbar)'' | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
==System Setup== | ==System Setup== | ||
| − | [[File: | + | [[File:Get Started Sys Set.jpg|512px|thumb|Initial Storage System setup procedures.]] |
| − | + | Setting up a new Storage System should always start by adding a license key in order to unlock all the core management features. | |
| + | Once a license to each system has been added be sure to change the 'admin' user password and then configure each network port with a static IP via the 'Storage Systems' section. | ||
| − | + | <br> | |
| − | -Step one guides one to | + | -Step one, "Add License", guides one to add a license key to enable storage management operations.<br><br> |
| − | -Step two guides one to activate a License.<br><br> | + | -Step two, "Activate License", guides one to activate a License.<br><br> |
| − | -Step three guides one to change the Administrator's Password.<br><br> | + | -Step three, "Set Password", guides one to change the Administrator's Password.<br><br> |
| − | + | <br><br><br><br><br><br><br> | |
| − | <br><br><br><br><br><br> | + | |
==Storage Grid Setup== | ==Storage Grid Setup== | ||
| − | [[File: | + | [[File:Get Started Stor Grid Set.jpg|512px|thumb|Storage Grid setup procedures.]] |
This procedure will assist with setting up a Storage Grid. Storage Grid technology makes it easy to manage large numbers of Storage Systems and enables access to features like remote-replication and scale-out storage. | This procedure will assist with setting up a Storage Grid. Storage Grid technology makes it easy to manage large numbers of Storage Systems and enables access to features like remote-replication and scale-out storage. | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| − | -Step one guides one to create a Storage Grid.<br><br> | + | -Step one, "Create a Storage Grid", guides one to create a Storage Grid.<br><br> |
| − | -Step two guides one to add Storage | + | -Step two, "Add System to Grid", guides one to add a Storage System to the Storage Grid.<br><br> |
| − | -Step three guides one to modify | + | -Step three, "Modify Grid Network Settings", guides one to modify grid network settings.<br><br> |
| − | -Step four guides one to configure the Alert Manager so as to send alert notifications to various devices.<br><br> | + | -Step four, "Configure Alerting", guides one to configure the Alert Manager so as to send alert notifications to various devices.<br><br> |
| − | -Step five(Optional) guides one to configure the | + | -Step five (Optional), "Configure Security Policy", guides one to configure the security policies.<br><br> |
| − | <br><br><br><br> | + | -Step six (Optional), "Join AD Domain", guides one to join an Active Directory (AD) domain to provide SMB access to AD users and AD groups.<br><br> |
| + | -Step seven (Optional), "Configure System Firewall", guides one to configure the network firewall settings. | ||
| + | <br><br> | ||
| − | == | + | ==Setup Storage Pool - Scale-up== |
| − | [[File: | + | [[File:Get Started Stor Pool Set.jpg|512px|thumb|Access to storage pools must be done via the associated VIFs to ensure continuous data availability in the event the pool is moved (failed-over) to another system.]] |
Storage pools formed from devices which are dual-connected to two storage systems may be made highly-available. This is done by creating a storage pool high-availability group to which one or more virtual network interfaces (VIFs) are added. All access to storage pools must be done via the associated VIFs to ensure continuous data availability in the event the pool is moved (failed-over) to another system. | Storage pools formed from devices which are dual-connected to two storage systems may be made highly-available. This is done by creating a storage pool high-availability group to which one or more virtual network interfaces (VIFs) are added. All access to storage pools must be done via the associated VIFs to ensure continuous data availability in the event the pool is moved (failed-over) to another system. | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| − | -Step one guides one to create a Site Cluster | + | -Step one, "Create Site Cluster", guides one to create a Site Cluster configuration for two or more Systems in the Storage Grid<br><br> |
| − | -Step two guides one to | + | -Step two, "Add Cluster Ring", guides one to create an additional Cluster Ring in the selected Site Cluster configuration.<br><br> |
| − | -Step three guides one to create a | + | -Step three, "Create Storage Pool", guides one to create in the selection of disks and configuration settings to create a new storage pool.<br><br> |
| − | -Step four guides one to create | + | -Step four, "Create HA Group", guides one to create an HA, Highly Available, group for Storage Pools. <br><br> |
| − | -Step five guides one to | + | -Step five, "Add Pool HA VIF", guides one to associate the storage pool with a High-availability Virtual Interfaces (HA VIF).<br> |
| − | <br><br><br> | + | |
| + | <br><br><br><br> | ||
| − | ==Scale-out | + | ==Setup Storage Pool - Scale-out Object== |
| − | [[File: | + | [[File:Get Started - Scale Out.jpg|512px|thumb|Setup Object Storage (Ceph RGW, '''R'''adow '''G'''ate'''w'''ay).]] |
| − | Scale-out | + | Scale-out object storage configurations deliver S3 object storage via S3-compatible buckets that may also be accessed as file storage via NFS. Object storage is typically setup with an erasure-coding layout to ensure fault-tolerance and high-availability. A scale-out storage cluster using three (3) or more Storage Systems must be setup first.<br><br> |
| − | + | -Step one, "Create Cluster", guides one to create Scale-out storage cluster.<br><br> | |
| − | -Step one guides one to create | + | -Step two, "Create OSDs & Journals", guides one to create '''O'''bject '''S'''torage '''D'''evices, OSDs.<br><br> |
| − | -Step two guides one to create '''O'''bject '''S'''torage '''D'''evices, | + | -Step three, "Create Object Storage Pool", guides one to create an S3 Object Storage Zone.<br><br> |
| − | -Step three guides one to create an S3 | + | -Step four, "Add S3 Gateway", guides one to select a Ceph Cluster for the S3 Gateway.<br><br> |
| − | -Step four guides one to select a Ceph Cluster for the S3 | + | -Step five, "Create S3 User", guides one to the creation of User Access Entries.<br><br> |
| − | -Step five guides one to the creation of User Access Entries.<br><br> | + | -Step six, "Create S3 Bucket", guides one to create one or more buckets for writing object storage via the S3 protocol.<br><br> |
| − | -Step six guides one to create | + | |
<br> | <br> | ||
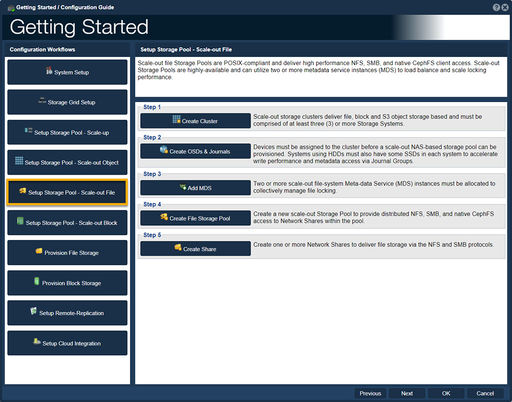
| − | ==Scale-out File | + | ==Setup Storage Pool - Scale-out File== |
| − | [[File: | + | [[File:Get Started - Scale-Out File.jpg|512px|thumb|Setup a Ceph File System (CephFS).]] |
The Ceph file system (CephFS) is a POSIX-compliant file system that uses a Ceph storage cluster to store its data. Ceph file systems are highly available using metadata servers (MDS). Once you have a healthy Ceph storage cluster with at least one Ceph metadata server, you can create a Ceph file system. | The Ceph file system (CephFS) is a POSIX-compliant file system that uses a Ceph storage cluster to store its data. Ceph file systems are highly available using metadata servers (MDS). Once you have a healthy Ceph storage cluster with at least one Ceph metadata server, you can create a Ceph file system. | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| − | -Step one guides one to Create a Scale-out Storage Cluster.<br><br> | + | -Step one, "Create Cluster", guides one to Create a Scale-out Storage Cluster.<br><br> |
| − | -Step two guides one to Create a Ceph '''O'''bject '''S'''torage '''D'''evice, OSD.<br><br> | + | -Step two, "Create OSDs & Journals", guides one to Create a Ceph '''O'''bject '''S'''torage '''D'''evice, OSD.<br><br> |
| − | -Step three guides one to Create a Ceph '''M'''eta '''D'''ata '''S'''erver, MDS.<br><br> | + | -Step three, "Add MDS", guides one to Create a Ceph '''M'''eta '''D'''ata '''S'''erver, MDS.<br><br> |
| − | -Step four | + | -Step four, "Create File Storage Pool", guides one to Create a Pool Profile.<br><br> |
| − | -Step five | + | -Step five, "Create Share", guides one to Create one or more Network Shares via NFS and SMB Protocols.<br><br> |
| − | + | <br><br><br><br> | |
| − | <br> | + | |
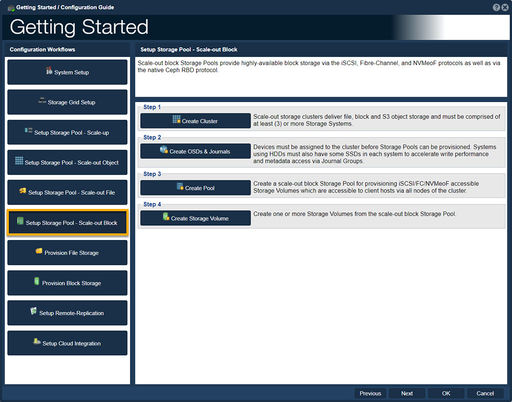
| − | ==Scale- | + | ==Setup Storage Pool - Scale-out Block== |
| − | [[File: | + | [[File:Get Started - Scale Out Block.jpg|512px|thumb|Setup Scale-out object and block storage.]] |
| − | Scale-out | + | Scale-out block Storage Pools provide highly-available block storage via the iSCSI, Fibre-Channel, and NVMeoF protocols as well as via the native Ceph RBD protocol.<br><br> |
| − | + | -Step one, "Create Cluster", guides one to create a Scale-out storage clusters deliver file, block and S3 object storage.<br><br> | |
| − | -Step one guides one to create a | + | -Step two, "Create OSDs & Journals", guides one to create '''O'''bject '''S'''torage '''D'''evices, OSD's and Journals.<br><br> |
| − | -Step two guides one to create '''O'''bject '''S'''torage '''D'''evices, OSD's.<br><br> | + | -Step three, "Create Pool", guides one create to a scale-out block Storage Pool for provisioning iSCSI/FC/NVMeoF accessible Storage Volumes which are accessible to client hosts via all nodes of the cluster.<br><br> |
| − | -Step three | + | -Step four, "Create Storage Volume", guides one to create a create one or more Storage Volumes from the scale-out block Storage Pool.<br><br><br><br><br> |
| − | + | <br><br> | |
| − | -Step | + | |
| − | <br><br><br> | + | |
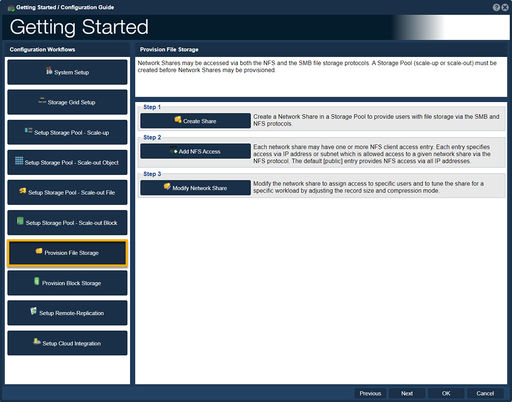
| − | ==Provision File Storage | + | ==Provision File Storage== |
| − | [[File: | + | [[File:Get Started - Prov File Stor.jpg|512px|thumb|Storage Pools (ZFS or CephFS) must be created before Network Shares may be provisioned]] |
| − | This procedure will assist with setting up Storage Pools and Volumes. | + | This procedure will assist with setting up Storage Pools and Volumes.<br><br> |
| − | -Step one | + | -Step one, "Create Share", guides one to create a Network Share in a Storage Pool.<br><br> |
| − | + | -Step two, "Add NFS Access", guides one to create NFS client entry access.<br><br> | |
| − | -Step | + | -Step three, "Modify Network Share", guides one to modify the network share to assign access to specific users and to tune the share for a specific workload.<br><br> |
| − | -Step | + | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | <br><br><br><br><br><br><br> | |
| − | + | ||
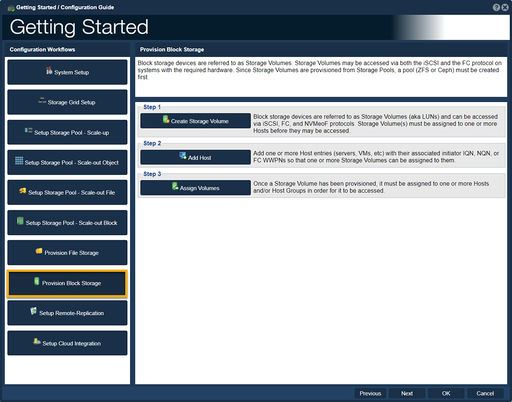
| − | File | + | ==Provision Block Storage== |
| + | [[File:Get Started - Prov Block Stor.jpg|512px|thumb|Setup Storage Volumes via iSCSI, FC, and NVMeoF protocols.]] | ||
| − | + | File storage folders are referred to as Network Shares. Network Shares may be accessed via both the NFS and the SMB protocols.<br><br> | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | ==Remote-Replication | + | -Step one, "Create Storage Volume", guides one to create a Storage Volume.<br><br> |
| − | [[File: | + | -Step two, "Add Host", guides one to add one or more host entries.<br><br> |
| + | -Step three, "Assign Volumes", guides one to assign Volume to one or more hosts.<br><br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br> | ||
| + | |||
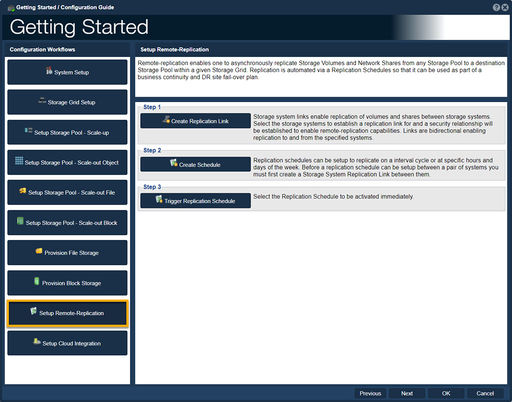
| + | ==Setup Remote-Replication== | ||
| + | [[File:Get Started - Setup Remote Rep.jpg|512px|thumb|Enable replication of volumes and shares between storage systems.]] | ||
Remote-Replication enables one to asynchronously replicate storage volumes and network shares from any storage pool to any destination storage pool within the storage grid. Replication is usually automated via a replication schedule so that it may be used as part of a business continuity and DR plan. | Remote-Replication enables one to asynchronously replicate storage volumes and network shares from any storage pool to any destination storage pool within the storage grid. Replication is usually automated via a replication schedule so that it may be used as part of a business continuity and DR plan. | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | -Step one guides one to create | + | <br> |
| − | -Step two guides one to create | + | |
| − | -Step three guides one to trigger a | + | -Step one, "Create Replication Link", guides one to create links for replication of volumes and shares between storage systems.<br><br> |
| − | <br><br><br><br><br><br><br> | + | -Step two, "Create Schedule", guides one to create schedules to replicate given specific interval cycles.<br><br> |
| + | -Step three, "Trigger Replication Schedule", guides one to immediately trigger a schedule. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br> | ||
| + | |||
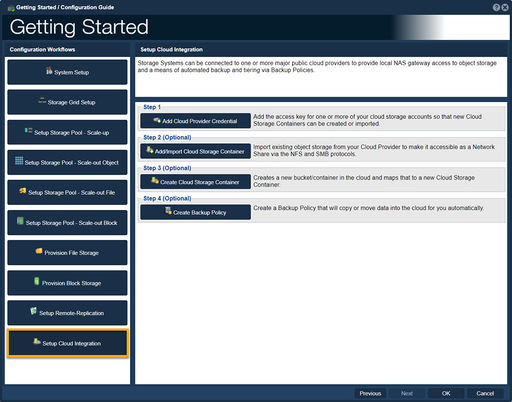
| + | ==Setup Cloud Integration== | ||
| + | [[File:Get Started - Cloud Intgrtn.jpg|512px|thumb|Integrate Cloud Storage.]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | QuantaStor integrates with all major public cloud providers to provide local NAS gateway access to object storage. This is done through the Cloud Container feature which also integrates with other features like Backup Policies.<br><br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | -Step one,"Add Cloud Provider Credential", guides one to add the access key for one or more of your cloud storage accounts.<br><br> | ||
| + | -Step two (Optional),"Add/Import Cloud Storage Container", guides one import existing object storage from your Cloud Provider.<br><br> | ||
| + | -Step three (Optional),"Create Cloud Storage Container", guides one to create a new bucket/container in the cloud and maps that to a new Cloud Storage Container.<br><br> | ||
| + | -Step four (Optional),"Create Backup Policy", guides one to create a Backup Policy that will copy or move data into the cloud for you automatically. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br><br><br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | For Additional Information... [https://wiki.osnexus.com/index.php?title=%2B_Getting_Started_Overview Getting Started Overview] | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | |||
{{Template:ReturnToWebGuide}} | {{Template:ReturnToWebGuide}} | ||
[[Category:Incomplete]] | [[Category:Incomplete]] | ||
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:QuantaStor6]] |
[[Category:WebUI Dialog]] | [[Category:WebUI Dialog]] | ||
Latest revision as of 10:14, 12 February 2024
The "Getting Started" or "Configuration Guide" in QuantaStor serves as a comprehensive resource that provides instructions, recommendations, and best practices for setting up and configuring QuantaStor storage management software.
The purpose of the "Getting Started" or "Configuration Guide" is to assist users in the initial setup and configuration of QuantaStor. It typically covers essential topics and tasks, such as:
- System Requirements: The guide outlines the hardware and software prerequisites for installing QuantaStor, including supported operating systems, storage controllers, and network configurations.
- Installation Process: It provides step-by-step instructions on how to install and deploy QuantaStor on the target hardware or virtual environment.
- Storage Pool Configuration: The guide explains how to create storage pools, define storage devices, and configure RAID levels or other data protection mechanisms.
- Storage Volume Management: It covers the creation, modification, and deletion of storage volumes within the storage pools, including various volume types and options available.
- Network Configuration: The guide may include information on configuring network interfaces, IP addresses, and network settings to enable proper connectivity and data access.
- Advanced Features: It may introduce advanced features and functionalities of QuantaStor, such as replication, thin provisioning, snapshots, or high-availability configurations.
- Best Practices: The guide often provides recommendations and best practices for optimizing performance, improving data reliability, and ensuring efficient management of the storage infrastructure.
The "Getting Started" or "Configuration Guide" aims to assist users in successfully setting up QuantaStor and getting their storage environment up and running. It serves as a valuable reference for understanding the various aspects of configuring and managing storage resources using QuantaStor's features and capabilities.
Navigation: Storage Management --> Storage System --> Storage System --> Getting Started (toolbar)
Contents
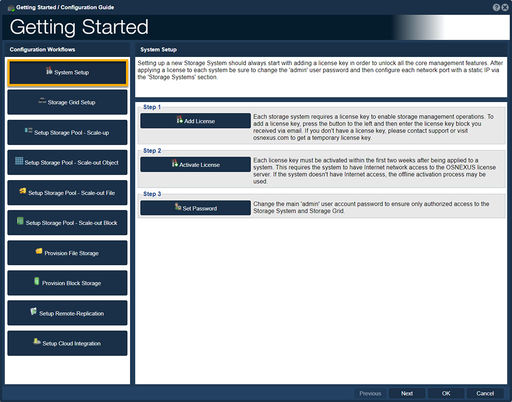
System Setup
Setting up a new Storage System should always start by adding a license key in order to unlock all the core management features. Once a license to each system has been added be sure to change the 'admin' user password and then configure each network port with a static IP via the 'Storage Systems' section.
-Step one, "Add License", guides one to add a license key to enable storage management operations.
-Step two, "Activate License", guides one to activate a License.
-Step three, "Set Password", guides one to change the Administrator's Password.
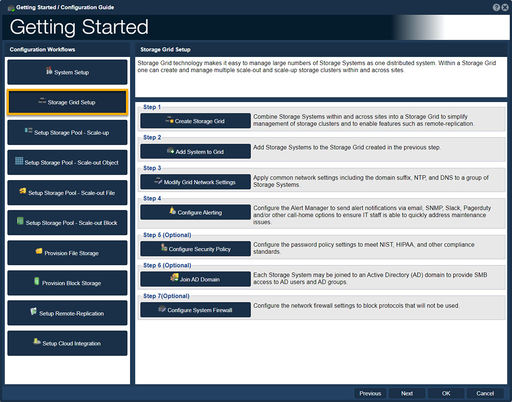
Storage Grid Setup
This procedure will assist with setting up a Storage Grid. Storage Grid technology makes it easy to manage large numbers of Storage Systems and enables access to features like remote-replication and scale-out storage.
-Step one, "Create a Storage Grid", guides one to create a Storage Grid.
-Step two, "Add System to Grid", guides one to add a Storage System to the Storage Grid.
-Step three, "Modify Grid Network Settings", guides one to modify grid network settings.
-Step four, "Configure Alerting", guides one to configure the Alert Manager so as to send alert notifications to various devices.
-Step five (Optional), "Configure Security Policy", guides one to configure the security policies.
-Step six (Optional), "Join AD Domain", guides one to join an Active Directory (AD) domain to provide SMB access to AD users and AD groups.
-Step seven (Optional), "Configure System Firewall", guides one to configure the network firewall settings.
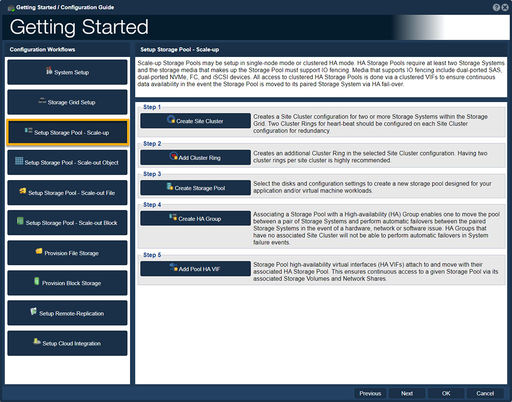
Setup Storage Pool - Scale-up
Storage pools formed from devices which are dual-connected to two storage systems may be made highly-available. This is done by creating a storage pool high-availability group to which one or more virtual network interfaces (VIFs) are added. All access to storage pools must be done via the associated VIFs to ensure continuous data availability in the event the pool is moved (failed-over) to another system.
-Step one, "Create Site Cluster", guides one to create a Site Cluster configuration for two or more Systems in the Storage Grid
-Step two, "Add Cluster Ring", guides one to create an additional Cluster Ring in the selected Site Cluster configuration.
-Step three, "Create Storage Pool", guides one to create in the selection of disks and configuration settings to create a new storage pool.
-Step four, "Create HA Group", guides one to create an HA, Highly Available, group for Storage Pools.
-Step five, "Add Pool HA VIF", guides one to associate the storage pool with a High-availability Virtual Interfaces (HA VIF).
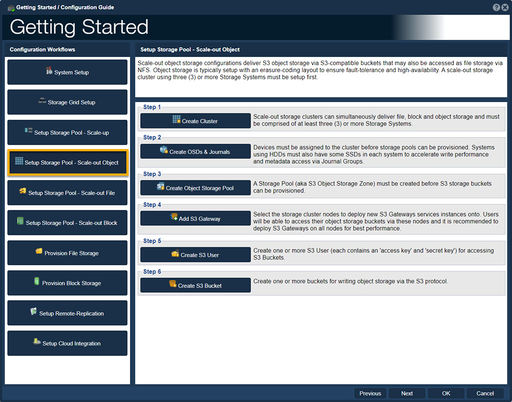
Setup Storage Pool - Scale-out Object
Scale-out object storage configurations deliver S3 object storage via S3-compatible buckets that may also be accessed as file storage via NFS. Object storage is typically setup with an erasure-coding layout to ensure fault-tolerance and high-availability. A scale-out storage cluster using three (3) or more Storage Systems must be setup first.
-Step one, "Create Cluster", guides one to create Scale-out storage cluster.
-Step two, "Create OSDs & Journals", guides one to create Object Storage Devices, OSDs.
-Step three, "Create Object Storage Pool", guides one to create an S3 Object Storage Zone.
-Step four, "Add S3 Gateway", guides one to select a Ceph Cluster for the S3 Gateway.
-Step five, "Create S3 User", guides one to the creation of User Access Entries.
-Step six, "Create S3 Bucket", guides one to create one or more buckets for writing object storage via the S3 protocol.
Setup Storage Pool - Scale-out File
The Ceph file system (CephFS) is a POSIX-compliant file system that uses a Ceph storage cluster to store its data. Ceph file systems are highly available using metadata servers (MDS). Once you have a healthy Ceph storage cluster with at least one Ceph metadata server, you can create a Ceph file system.
-Step one, "Create Cluster", guides one to Create a Scale-out Storage Cluster.
-Step two, "Create OSDs & Journals", guides one to Create a Ceph Object Storage Device, OSD.
-Step three, "Add MDS", guides one to Create a Ceph Meta Data Server, MDS.
-Step four, "Create File Storage Pool", guides one to Create a Pool Profile.
-Step five, "Create Share", guides one to Create one or more Network Shares via NFS and SMB Protocols.
Setup Storage Pool - Scale-out Block
Scale-out block Storage Pools provide highly-available block storage via the iSCSI, Fibre-Channel, and NVMeoF protocols as well as via the native Ceph RBD protocol.
-Step one, "Create Cluster", guides one to create a Scale-out storage clusters deliver file, block and S3 object storage.
-Step two, "Create OSDs & Journals", guides one to create Object Storage Devices, OSD's and Journals.
-Step three, "Create Pool", guides one create to a scale-out block Storage Pool for provisioning iSCSI/FC/NVMeoF accessible Storage Volumes which are accessible to client hosts via all nodes of the cluster.
-Step four, "Create Storage Volume", guides one to create a create one or more Storage Volumes from the scale-out block Storage Pool.
Provision File Storage
This procedure will assist with setting up Storage Pools and Volumes.
-Step one, "Create Share", guides one to create a Network Share in a Storage Pool.
-Step two, "Add NFS Access", guides one to create NFS client entry access.
-Step three, "Modify Network Share", guides one to modify the network share to assign access to specific users and to tune the share for a specific workload.
Provision Block Storage
File storage folders are referred to as Network Shares. Network Shares may be accessed via both the NFS and the SMB protocols.
-Step one, "Create Storage Volume", guides one to create a Storage Volume.
-Step two, "Add Host", guides one to add one or more host entries.
-Step three, "Assign Volumes", guides one to assign Volume to one or more hosts.
Setup Remote-Replication
Remote-Replication enables one to asynchronously replicate storage volumes and network shares from any storage pool to any destination storage pool within the storage grid. Replication is usually automated via a replication schedule so that it may be used as part of a business continuity and DR plan.
-Step one, "Create Replication Link", guides one to create links for replication of volumes and shares between storage systems.
-Step two, "Create Schedule", guides one to create schedules to replicate given specific interval cycles.
-Step three, "Trigger Replication Schedule", guides one to immediately trigger a schedule.
Setup Cloud Integration
QuantaStor integrates with all major public cloud providers to provide local NAS gateway access to object storage. This is done through the Cloud Container feature which also integrates with other features like Backup Policies.
-Step one,"Add Cloud Provider Credential", guides one to add the access key for one or more of your cloud storage accounts.
-Step two (Optional),"Add/Import Cloud Storage Container", guides one import existing object storage from your Cloud Provider.
-Step three (Optional),"Create Cloud Storage Container", guides one to create a new bucket/container in the cloud and maps that to a new Cloud Storage Container.
-Step four (Optional),"Create Backup Policy", guides one to create a Backup Policy that will copy or move data into the cloud for you automatically.
For Additional Information... Getting Started Overview