Difference between revisions of "IBM Cloud Provisioning Guide"
m (→Sizing the License) |
m (→Selecting and Configuring Boot System Drives) |
||
| Line 73: | Line 73: | ||
If you want to calculate the correct license capacity based on a target ''usable'' capacity, the Solution Design tool [https://www.osnexus.com/design-ibm] will help you design a QuantaStor storage server using IBM Cloud Bare Metal hardware and select the optimal license. | If you want to calculate the correct license capacity based on a target ''usable'' capacity, the Solution Design tool [https://www.osnexus.com/design-ibm] will help you design a QuantaStor storage server using IBM Cloud Bare Metal hardware and select the optimal license. | ||
| − | == Selecting and Configuring | + | == Selecting and Configuring Storage Disks == |
| − | Create | + | I. Create a RAID1 Array for OS Boot Drives |
*Step 1. Select "RAID1" under Type | *Step 1. Select "RAID1" under Type | ||
| − | *Step 2. Enter the | + | *Step 2. Enter the Quantity "2" under # Disks |
*Step 3. Select SATA under Disk Media | *Step 3. Select SATA under Disk Media | ||
| Line 84: | Line 84: | ||
*Step 4. Select 1 TB under Disk Size | *Step 4. Select 1 TB under Disk Size | ||
| − | Add Storage disks | + | II. Add Storage disks |
| − | *Step 5. Click on Add New + | + | *Step 5. Click on "Add New +" Button |
| − | *Step 6. Select JBOD under Type | + | *Step 6. Select "Individual" or "JBOD" under Type |
| − | *Step 7. Enter the | + | *Step 7. Enter the desired Quantity under # Disks |
| − | *Step 8. Select your desired Disk Media ( | + | *Step 8. Select your desired SATA, SAS or SSD Disk Media (all IBM Cloud Bare Metal storage media are supported) |
*Step 9. Select your desired Disk Size | *Step 9. Select your desired Disk Size | ||
| − | *Step 10. Repeat steps 5 through 9 as | + | *Step 10. Repeat steps 5 through 9 as required for each individual disk media/size you require. Do not forget any SSD read and write cache devices for hybrid configurations! |
| − | QuantaStor manages | + | '''IMPORTANT!!'''<br> |
| + | QuantaStor directly manages the RAID/erasure-encoding of the data storage media. The onboard server RAID controller is used to format the OS boot drives only (Process I), all subsequent drive entries during the Bare Metal configuration process should be set to "Individual" or "JBOD" (Process II). | ||
[[File:Ibmc_disk_select.png|1024px]] | [[File:Ibmc_disk_select.png|1024px]] | ||
Revision as of 13:29, 14 May 2019
Contents
- 1 Overview
- 2 Selecting a QuantaStor Server Chassis
- 3 Selecting RAM Quantity for Mixed or Read-heavy Workloads
- 4 Selecting a CPU for Mixed or Read-heavy Workloads
- 5 Selecting an IBM Cloud Data Center
- 6 Correctly Sizing a QuantaStor License
- 7 Selecting and Configuring Storage Disks
- 8 Network Configuration
- 9 Server Login
Overview
The following Provisioning Guide details the process of selecting hardware for your QuantaStor system using IBM Cloud's Bare Metal online ordering tools. Reference Configurations for SAN/NAS Appliances, Scale-out Object and Scale-out Block appliances or Scale-out NAS Appliances can be found here. Complete technical documentation for QuantaStor can be found here.
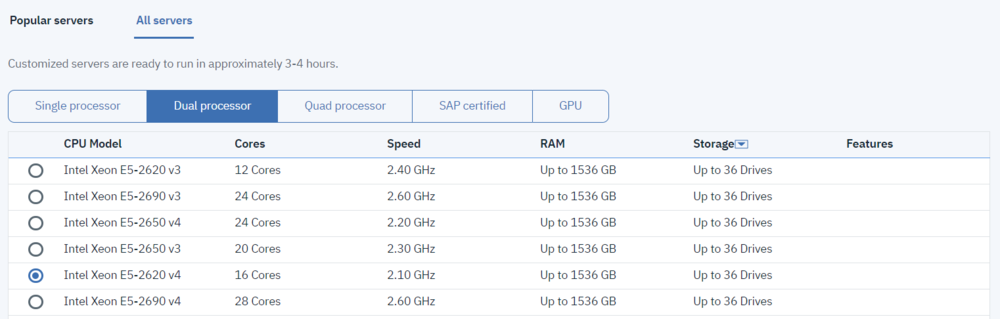
Selecting a QuantaStor Server Chassis
The provisioning of your QuantaStor solution in the IBM Cloud begins with the selection of a Bare Metal server chassis suitable for your workload:
- In your web browser, navigate to https://www.ibm.com/cloud/bare-metal-servers and click on "Customize your server"
- Chose the "All servers" option
- Chose the "Dual processor" option and sort (in descending order) by "Storage"
Note: The best chassis options for QuantaStor use are the 12-bay and 36-bay server models. The 36-bay is recommended due to its greater configuration flexibility, cost-effectiveness, and maximum storage capacity. In general, the 8 and 12-bay chassis should only be chosen for small-scale or all-SSD/NVMe high-performance use-cases, while the 36-bay chassis can be ordered less than fully populated and can be expanded by adding new disks at a future date.
When selecting the correct server chassis for a deployment, follow these general guidelines:
- If the number of storage drives (not OS, not hot-spare) needed is > 10 you'll need to use the 36-bay chassis
- If the usable storage capacity required is > 48 TB or expected to grow beyond that, use the 36-bay chassis
- If using a scale up SAN/NAS configuration and any significant expansion in storage capacity needs is expected within the first 12 months of deployment, go with the 36-bay chassis
- If the deployment is a scale-out block, object or file configuration using spinning disks, use the 36-bay chassis
- If storage expansion is an "unknown", go with the 36-bay chassis!
- If the storage configuration is all-SSD or NVMe, an 8-bay or 12-bay chassis may provide better performance for your clients
- If the maximum expected capacity is under 48 TB, the 8 or 12-bay chassis should suffice
Selecting RAM Quantity for Mixed or Read-heavy Workloads
- For most SAN/NAS workloads the ideal ratio of RAM to usable capacity is 1GB RAM per 1TB of storage.
- Backup & Archive use cases require less at 300MB-500MB per 1TB.
- While there is no maximum RAM limit, free RAM is used as a read cache which can greatly benefit many workloads.
- For scale-out block, and object solutions, add 1 GB of RAM per physical disk (Ceph OSD).
Use the IBM Cloud solution design tools [1] to automatically select the optimal amount of RAM for your use case:
Selecting a CPU for Mixed or Read-heavy Workloads
- OSNEXUS recommends the use of dual-processor configurations.
- Both SAN/NAS and Scale-out solutions benefit from higher clock speeds and greater core counts (though 8 & 12-bay chassis need a higher-end processor only when deploying an all-flash configuration).
- If this will be an all-flash node, or for all latency-sensitive, high performance workloads, opt for the highest clock speed available within budget.
- Scale-out block and object configurations generally require 1GHz core per storage device. A system with 30 disks will require about double the CPU power of a system with 12 disks.
- Systems with encryption enabled will benefit from the selection of a faster CPU. Typical performance degradation from encrypted storage pools is 10-20%.
- QuantaStor does not recommend the use of quad processor configurations in any environment.
The QuantaStor for IBM Cloud solution design tool [2] will select the optimal CPU automatically for you:
Selecting an IBM Cloud Data Center
Network latency is a key factor in storage performance on nearly any protocol and intended workload, thus geographic proximity is important. You will want to deploy a QuantaStor storage server in the same location as the most performance-demanding of your application servers. If the application servers are in a remote site, locate the QuantaStor appliance in the data center to nearest to the application server. Be sure to select the correct data center for your intended use-case, and verify your desired server option is available at that location.
Correctly Sizing a QuantaStor License
QuantaStor Cloud Edition license subscriptions are based on raw capacity amounts:
- XS = up to 4TB
- SM = up to 16TB
- MD = up to 48TB
- LG = up to 128TB
- XL = up to 256TB
- XXL = up to 384TB
- Be sure to choose a QuantaStor license with capacity equal to (or larger than) the size of your intended storage pool (= disk capacity x no. of disks).
- License calculations are based on the storage capacity under management, before application of RAID formatting or erasure encoding.
- License calculations count only disks actively used to form the storage pool, thereby excluding hot-spares, cold-spares and boot devices.
- Simply sum up the capacities for every data, journal and cache disk and choose a license capacity that is equal to or above that number.
If you want to calculate the correct license capacity based on a target usable capacity, the Solution Design tool [3] will help you design a QuantaStor storage server using IBM Cloud Bare Metal hardware and select the optimal license.
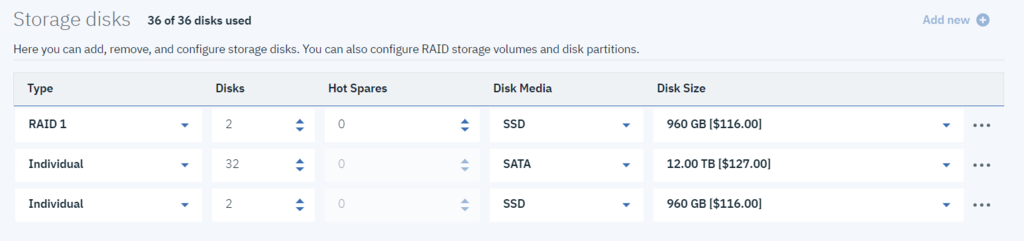
Selecting and Configuring Storage Disks
I. Create a RAID1 Array for OS Boot Drives
- Step 1. Select "RAID1" under Type
- Step 2. Enter the Quantity "2" under # Disks
- Step 3. Select SATA under Disk Media
- Step 4. Select 1 TB under Disk Size
II. Add Storage disks
- Step 5. Click on "Add New +" Button
- Step 6. Select "Individual" or "JBOD" under Type
- Step 7. Enter the desired Quantity under # Disks
- Step 8. Select your desired SATA, SAS or SSD Disk Media (all IBM Cloud Bare Metal storage media are supported)
- Step 9. Select your desired Disk Size
- Step 10. Repeat steps 5 through 9 as required for each individual disk media/size you require. Do not forget any SSD read and write cache devices for hybrid configurations!
IMPORTANT!!
QuantaStor directly manages the RAID/erasure-encoding of the data storage media. The onboard server RAID controller is used to format the OS boot drives only (Process I), all subsequent drive entries during the Bare Metal configuration process should be set to "Individual" or "JBOD" (Process II).
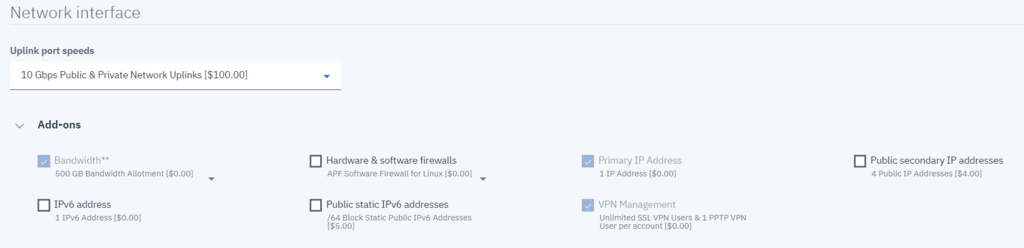
Network Configuration
While QuantaStor does support all IBM SoftLayer options for network configuration, in most use-cases where all or the bulk of client throughput will come from your other servers and VM's at IBM SoftLayer, OSNEXUS recommends opting for the *Private Network Only* set of choices in order to double up the available back-end bandwidth. Unless constant, low-latency accessibility to the storage via the whole public internet is a requirement, OSNEXUS' recommends *Private Network Only* still be used even when irregular internet access is required, and another server or VM be deployed (or turned online only as necessary) to provide gateway/VPN/intermediary access to the storage.
IBM Cloud/SoftLayer maintains an internal upgrade software repository accessible via their private network for all QuantaStor customers, which will be automatically pre-configured. You do not require a public network connection to receive software updates in IBM Cloud/SoftLayer.
Complete QuantaStor Server Configuration
You mean run into a situation where the Checkout button is not visible, in such cases, try scrolling horizontally to the right.
Server Login
Once deployment has been completed you should get a notification from IBM. Check your account for login credentials and IP information. The QuantaStor Web UI should be listening on every initially provisioned IP address, if you do not get the login prompt in your browser, verify you have VPN connectivity to your IBM Cloud backend network. You can find additional information on QuantaStor setup in the Getting Started Overview, as well as the Administrator's Guide