Difference between revisions of "Clustered HA SAN/NAS Solutions using ZFS"
m (→HA Virtual Network Interface creation) |
m |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | + | __TOC__ | |
| + | <!-- Removed Overview header, replaced with Introduction and reduced to H2 for TOC alignment/navigation --> | ||
| + | == Introduction == | ||
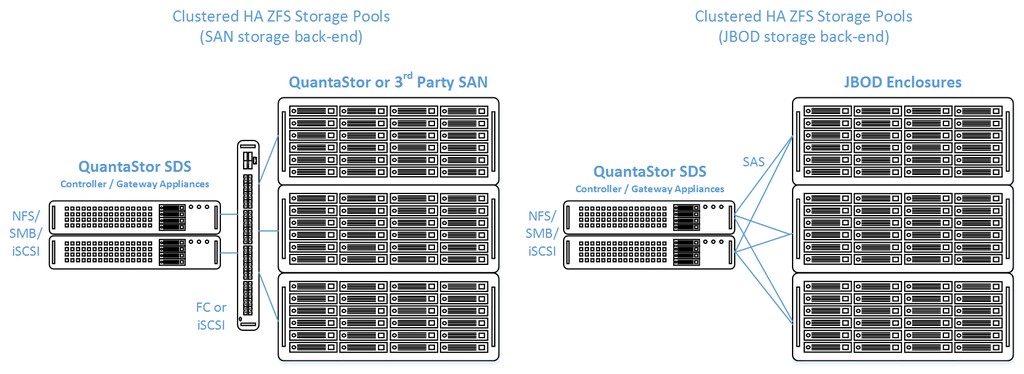
QuantaStor's clustered storage pool configurations ensure high-availability (HA) in the event of a node outage or storage connectivity to the active node is lost. From a hardware perspective a QuantaStor deployment of one or more clustered storage pools requires at least two QuantaStor appliances so that automatic fail-over can occur in the event that the active appliance goes offline. Another requirement of these configurations is that the disk storage devices for the highly-available pool cannot be in either of the server units. Rather the storage must come from an external source which can be as simple as using one or more SAS JBOD enclosures or for higher performance configurations could be a SAN delivering block storage (LUNs) to the QuantaStor front-end appliances over FC (preferred) or iSCSI. The following two sections outline the minimum hardware requirements for each. | QuantaStor's clustered storage pool configurations ensure high-availability (HA) in the event of a node outage or storage connectivity to the active node is lost. From a hardware perspective a QuantaStor deployment of one or more clustered storage pools requires at least two QuantaStor appliances so that automatic fail-over can occur in the event that the active appliance goes offline. Another requirement of these configurations is that the disk storage devices for the highly-available pool cannot be in either of the server units. Rather the storage must come from an external source which can be as simple as using one or more SAS JBOD enclosures or for higher performance configurations could be a SAN delivering block storage (LUNs) to the QuantaStor front-end appliances over FC (preferred) or iSCSI. The following two sections outline the minimum hardware requirements for each. | ||
[[File:qs_clustered_san.png|1024px]] | [[File:qs_clustered_san.png|1024px]] | ||
| − | === Configuration | + | === Setup and Configuration Overview === |
| + | <!-- Using 'Overview' here instead of 'Summary' will clarify this is not a perform-these-steps section --> | ||
| + | * Install both QuantaStor Appliances with the most recent release of QuantaStor. | ||
| + | ** Apply the QuantaStor Gold, Platinum or Cloud Edition license key to each appliance. Each key must be unique. | ||
| + | ** Create a Grid and join both QuantaStor Appliances to the grid. | ||
| − | * | + | * Configure SAS Hardware and Verify connectivity of SAS cables from HBAs to JBOD |
| − | + | ** LSI SAS HBA's must be configured with the 'Boot Support' MPT BIOS option configured to 'OS only' mode. | |
| − | * | + | ** Verify that the SAS disks installed in both systems appear to both head nodes in the WebUI Hardware Enclosures and Controllers section. |
| − | * | + | |
| − | * | + | |
| − | * | + | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | * Create Network and Cluster heartbeat configuration and Verify network connectivity | |
| + | ** At least two NICs are required for a HA Cluster configuration with separate networks | ||
| − | * | + | * Create a Storage Pool |
| − | * | + | ** Use only drives from shared storage |
| − | * | + | |
| − | + | * Create Storage Pool HA Group | |
| + | * Create one or more Storage Pool HA Virtual Interfaces | ||
| + | * Activate the Storage Pool | ||
| + | * Test failover | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | == High Availability Tiered SAN/ZFS based SAN/NAS Storage Layout == | |
| − | == | + | |
In this configuration the QuantaStor front-end controller appliances are acting as a ''gateway'' to the storage in the SANs on the back-end. QuantaStor has been tested with NetApp and HP MSA 3rd party SANs as back-end storage as well as with QuantaStor SDS as a back-end SAN. Please contact support@osnexus.com for the latest HCL for 3rd party SAN support or to get additional SAN support added to the HCL. | In this configuration the QuantaStor front-end controller appliances are acting as a ''gateway'' to the storage in the SANs on the back-end. QuantaStor has been tested with NetApp and HP MSA 3rd party SANs as back-end storage as well as with QuantaStor SDS as a back-end SAN. Please contact support@osnexus.com for the latest HCL for 3rd party SAN support or to get additional SAN support added to the HCL. | ||
| Line 43: | Line 44: | ||
==== All Appliances ==== | ==== All Appliances ==== | ||
| + | * Login to the QuantaStor web management interface on each appliance | ||
* Add your license keys, one unique key for each appliance | * Add your license keys, one unique key for each appliance | ||
* Setup static IP addresses on each appliance (DHCP is the default and should only be used to get the appliance initially setup) | * Setup static IP addresses on each appliance (DHCP is the default and should only be used to get the appliance initially setup) | ||
| Line 48: | Line 50: | ||
==== Back-end Appliances (Data Nodes) ==== | ==== Back-end Appliances (Data Nodes) ==== | ||
| − | * Setup each back-end ''data node'' appliance as per basic appliance configuration with one or more storage pools each with one storage volume per pool. | + | * Setup each back-end ''data node'' appliance as per basic appliance configuration with one or more storage pools, each with one storage volume per pool. |
** Ideal pool size is 10 to 20 drives, you may need to create multiple pools per back-end appliance. | ** Ideal pool size is 10 to 20 drives, you may need to create multiple pools per back-end appliance. | ||
** SAS is recommended but enterprise SATA drives can also be used | ** SAS is recommended but enterprise SATA drives can also be used | ||
| Line 55: | Line 57: | ||
==== Front-end Appliances (Controller Nodes) ==== | ==== Front-end Appliances (Controller Nodes) ==== | ||
* Connectivity between the front-end and back-end nodes can be FC or iSCSI | * Connectivity between the front-end and back-end nodes can be FC or iSCSI | ||
| + | |||
===== FC SAN Back-end Configuration ===== | ===== FC SAN Back-end Configuration ===== | ||
* Create ''Host'' entries, one for each front-end appliance and add the WWPN of each of the FC ports on the front-end appliances which will be used for intercommunication between the front-end and back-end nodes. | * Create ''Host'' entries, one for each front-end appliance and add the WWPN of each of the FC ports on the front-end appliances which will be used for intercommunication between the front-end and back-end nodes. | ||
* Direct point-to-point physical cabling connections can be made in smaller configurations to avoid the cost of an FC switch. Here's a guide that can help with some [http://blog.osnexus.com/2012/03/20/understanding-fc-fabric-configuration-5-paragraphs/ advice on FC zone setup] for larger configurations using a back-end fabric. | * Direct point-to-point physical cabling connections can be made in smaller configurations to avoid the cost of an FC switch. Here's a guide that can help with some [http://blog.osnexus.com/2012/03/20/understanding-fc-fabric-configuration-5-paragraphs/ advice on FC zone setup] for larger configurations using a back-end fabric. | ||
| − | * If you're using a FC switch you should use a fabric topology that | + | * If you're using a FC switch you should use a fabric topology that will give you fault tolerance. |
* Back-end appliances must use Qlogic QLE 8Gb or 16Gb FC cards as QuantaStor can only present Storage Volumes as FC target LUNs via Qlogic cards. | * Back-end appliances must use Qlogic QLE 8Gb or 16Gb FC cards as QuantaStor can only present Storage Volumes as FC target LUNs via Qlogic cards. | ||
===== iSCSI SAN Back-end Configuration ===== | ===== iSCSI SAN Back-end Configuration ===== | ||
| − | * It | + | * It is highly recommended to separate the networks for the front-end (client communication) vs back-end (communicate between the control and data appliances). |
* For iSCSI connectivity to the back-end nodes, create a ''Software iSCSI Adapter'' by going to the Hardware Controllers & Enclosures section and adding a iSCSI Adapter. This will take care of logging into and accessing the back-end storage. The back-end storage appliances must assign their Storage Volumes to all the ''Hosts'' for the front-end nodes with their associated iSCSI IQNs. | * For iSCSI connectivity to the back-end nodes, create a ''Software iSCSI Adapter'' by going to the Hardware Controllers & Enclosures section and adding a iSCSI Adapter. This will take care of logging into and accessing the back-end storage. The back-end storage appliances must assign their Storage Volumes to all the ''Hosts'' for the front-end nodes with their associated iSCSI IQNs. | ||
* Right-click to Modify Network Port of each port you want to disable client iSCSI access on. If you have 10GbE be sure to disable iSCSI access on the slower 1GbE ports used for management access and/or remote-replication. | * Right-click to Modify Network Port of each port you want to disable client iSCSI access on. If you have 10GbE be sure to disable iSCSI access on the slower 1GbE ports used for management access and/or remote-replication. | ||
| Line 73: | Line 76: | ||
* Create a ''Storage Pool'' on the first front-end appliance (ZFS based) using the ''physical disks'' which have arrived from the back-end appliances. | * Create a ''Storage Pool'' on the first front-end appliance (ZFS based) using the ''physical disks'' which have arrived from the back-end appliances. | ||
** QuantaStor will automatically analyze the disks from the back-end appliances and stripe across the appliances to ensure proper fault-tolerance across the back-end nodes. | ** QuantaStor will automatically analyze the disks from the back-end appliances and stripe across the appliances to ensure proper fault-tolerance across the back-end nodes. | ||
| − | * Create a ''Storage Pool HA Group'' for the pool created in the previous step | + | * Create a ''Storage Pool HA Group'' for the pool created in the previous step. If the storage is not accessible to both appliances, it will block you from creating the group. |
* Create a Storage Pool Virtual Interface for the Storage Pool HA Group. All NFS/iSCSI access to the pool must be through the Virtual Interface IP address to ensure highly-available access to the storage for the clients. | * Create a Storage Pool Virtual Interface for the Storage Pool HA Group. All NFS/iSCSI access to the pool must be through the Virtual Interface IP address to ensure highly-available access to the storage for the clients. | ||
* Enable the Storage Pool HA Group. Automatic Storage Pool fail-over to the passive node will now occur if the active node is disabled or heartbeat between the nodes is lost. | * Enable the Storage Pool HA Group. Automatic Storage Pool fail-over to the passive node will now occur if the active node is disabled or heartbeat between the nodes is lost. | ||
| Line 87: | Line 90: | ||
[[File:osn_clustered_san_config.png|640px]] | [[File:osn_clustered_san_config.png|640px]] | ||
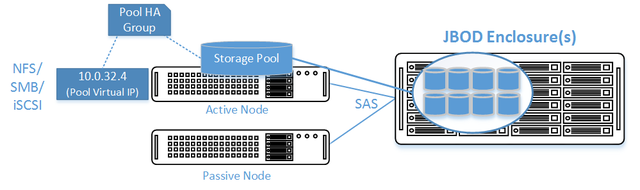
| − | == | + | == High Availability Shared JBOD/ZFS based SAN/NAS Storage Layout == |
[[File:qs_clustered_jbod_minimum_hardware.png|640px]] | [[File:qs_clustered_jbod_minimum_hardware.png|640px]] | ||
| Line 105: | Line 108: | ||
=== Setup Process === | === Setup Process === | ||
| − | ==== | + | ==== All Appliances ==== |
* Login to the QuantaStor web management interface on each appliance | * Login to the QuantaStor web management interface on each appliance | ||
* Add your license keys, one unique key for each appliance | * Add your license keys, one unique key for each appliance | ||
* Setup static IP addresses on each node (DHCP is the default and should only be used to get the appliance initially setup) | * Setup static IP addresses on each node (DHCP is the default and should only be used to get the appliance initially setup) | ||
* Right-click to Modify Network Port of each port you want to disable iSCSI access on. If you have 10GbE be sure to disable iSCSI access on the slower 1GbE ports used for management access and/or remote-replication. | * Right-click to Modify Network Port of each port you want to disable iSCSI access on. If you have 10GbE be sure to disable iSCSI access on the slower 1GbE ports used for management access and/or remote-replication. | ||
| + | |||
==== [[Clustered_HA_SAN/NAS_(ZFS_based)_Storage_Pool_Setup#Site_Cluster_Network_Requirements|Heartbeat/Cluster Network Configuration]] ==== | ==== [[Clustered_HA_SAN/NAS_(ZFS_based)_Storage_Pool_Setup#Site_Cluster_Network_Requirements|Heartbeat/Cluster Network Configuration]] ==== | ||
* Right-click on the storage system and set the DNS IP address (eg 8.8.8.8), and your NTP server IP address | * Right-click on the storage system and set the DNS IP address (eg 8.8.8.8), and your NTP server IP address | ||
| Line 132: | Line 136: | ||
[[File:osn_clustered_jbod_config.png|640px]] | [[File:osn_clustered_jbod_config.png|640px]] | ||
| − | + | == Site Cluster Configuration == | |
| − | + | ||
| − | == Site Cluster | + | |
The Site Cluster represents a group of two or more appliances that have an active heartbeat mechanism which is used to activate resource fail-over in the event that a resource (storage pool) goes offline. Site Clusters should be comprised of QuantaStor appliances which are all in the same location but could span buildings within the same site. The heartbeat expects a low latency connection and is typically done via dual direct Ethernet cable connections between a pair of QuantaStor appliances but could also be done with Ethernet switches in-between. | The Site Cluster represents a group of two or more appliances that have an active heartbeat mechanism which is used to activate resource fail-over in the event that a resource (storage pool) goes offline. Site Clusters should be comprised of QuantaStor appliances which are all in the same location but could span buildings within the same site. The heartbeat expects a low latency connection and is typically done via dual direct Ethernet cable connections between a pair of QuantaStor appliances but could also be done with Ethernet switches in-between. | ||
[[File:qs_heartbeat_rings.png]] | [[File:qs_heartbeat_rings.png]] | ||
| − | + | <!-- Section needs to be moved to an Admin Guide or other location | |
=== Use Cases for Site Clusters === | === Use Cases for Site Clusters === | ||
| Line 151: | Line 153: | ||
:: [[File:qs_site_gluster_ip.png|600px]] | :: [[File:qs_site_gluster_ip.png|600px]] | ||
:: In these configurations all appliance nodes which are used to provide storage to the Gluster volume should be members of the Site Cluster. | :: In these configurations all appliance nodes which are used to provide storage to the Gluster volume should be members of the Site Cluster. | ||
| + | -- Move Section --> | ||
| + | <!-- Once moved, a good inclusion would be a link to the new section: | ||
| + | * For more information about Site Cluster use cases, please see the [[Section We Moved The Site Cluster Use Cases To]]. | ||
| + | --> | ||
=== Grid Setup === | === Grid Setup === | ||
Both appliances must be in the same grid before the Site Cluster can be created. Grid creation takes less than a minute and the buttons to create the grid and add a second node to the grid are in the ribbon bar. QuantaStor appliances can only be members of a single grid at a time but up to 64 appliances can be added to a grid which can contain multiple independent Site Clusters. | Both appliances must be in the same grid before the Site Cluster can be created. Grid creation takes less than a minute and the buttons to create the grid and add a second node to the grid are in the ribbon bar. QuantaStor appliances can only be members of a single grid at a time but up to 64 appliances can be added to a grid which can contain multiple independent Site Clusters. | ||
| Line 157: | Line 163: | ||
[[File:qs_create_ha_grid.png]] | [[File:qs_create_ha_grid.png]] | ||
| − | === Site Cluster Network | + | === Site Cluster Network Configuration === |
| − | + | <!-- Title unifies with subsequent sections and clarifies this is the setup/config detail --> | |
| + | Before beginning, note that when you create the Site Cluster it will automatically create the first heartbeat ring (Cluster Ring) on the network that you have specified. This can be a direct connect private network between two appliances or the ports could be connected to a switch. The key requirement is that the '''name of the ports used for the Cluster Ring must be the same'''. For example, if eth0 is the port on '''Appliance A''' with IP '''10.3'''.0.5/16 then you must configure the matching eth0 network port on '''Appliance B''' with an IP on the same network (10.3.0.0/16), for example '''10.3'''.0.7/16. | ||
* Each Highly Available Virtual Network Interface requires Three IP Addresses be configured in the same subnet: one for the Virtual Network Interface and one for each Network Device on each QuantaStor Storage Appliance. | * Each Highly Available Virtual Network Interface requires Three IP Addresses be configured in the same subnet: one for the Virtual Network Interface and one for each Network Device on each QuantaStor Storage Appliance. | ||
| Line 172: | Line 179: | ||
=== Creating the Site Cluster === | === Creating the Site Cluster === | ||
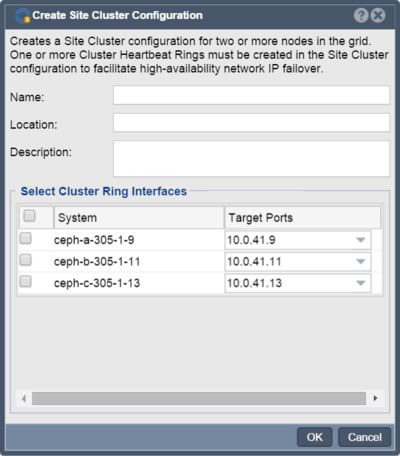
| − | The | + | The Site Cluster name is a required field and can be set to anything you like, for example '''ha-pool-cluster'''. The location and description fiels are optional. Note that all of the network ports selected are on the same subnet with unique IPs for each node. These are the IP addresses that will be used for heartbeat communication. Client communication will be handled later in the Creating a Virtual IP in the Storage Pool HA Group section. |
[[File:qs_site_cluster_create.png|400px]] | [[File:qs_site_cluster_create.png|400px]] | ||
| Line 178: | Line 185: | ||
=== Dual Heartbeat Rings Required === | === Dual Heartbeat Rings Required === | ||
| − | + | Any cluster intended for production deployment must have at least two heartbeat Cluster Rings configured. Configurations using a single heartbeat Cluster Ring are fragile and are only suitable for test configurations not intended for production use. Without dual rings in place, it is very easy for a false positive failover event to occur, making any network changes likely to activate a fail-over inadvertently. | |
| − | + | After creating the Site Cluster, an initial Cluster Ring will exist. Proceed by creating a second one by choosing 'Add Cluster Ring' from the toolbar. | |
| + | |||
| + | [[File:qs_cluster_ring_add.png|1024px]] | ||
== Cluster HA Storage Pool Creation == | == Cluster HA Storage Pool Creation == | ||
| Line 187: | Line 196: | ||
=== Disk Connectivity Pre-checks === | === Disk Connectivity Pre-checks === | ||
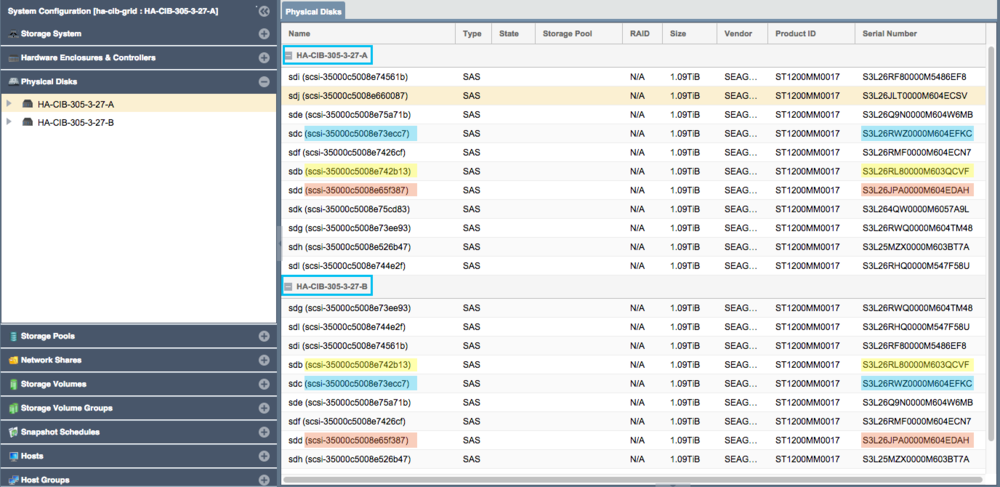
| − | Any storage Storage Pool which is to be made | + | Any storage Storage Pool which is to be made Highly-Available must be configured such that both appliances used in the HA configuration both have access to all disks used by the storage pool. This necessarily requires that all devices used by a storage pool (including cache, log, and hot-spare devices) must be in a ''shared'' external JBOD or SAN. Verify connectivity to the back-end storage used by the Storage Pool via the ''Physical Disks'' section. |
| − | [[File: | + | [[File:Qs_ha_verify_disks_shared_nopool.png|1000px]] |
| − | Note how | + | * Note how devices with the same ID/Serial Numbers are visible on both storage appliances. This is a strict requirement for creating Storage Pool HA Groups. |
| + | * Dual-ported SAS drives must be used when deploying a HA configuration with a JBOD backend. | ||
| + | * Enterprise and Data Center (DC) grade SATA drives can be used in a Tiered SAN HA configuration with QuantaStor appliances used as back-end storage rather than a JBOD. | ||
=== Storage Pool Creation (ZFS) === | === Storage Pool Creation (ZFS) === | ||
| − | + | Once the disks have been verified as visible to both nodes in the cluster, proceed with Storage Pool creation using the following steps: | |
* Configure the Storage Pool on one of the nodes using the Create Storage Pool dialog. | * Configure the Storage Pool on one of the nodes using the Create Storage Pool dialog. | ||
| Line 204: | Line 215: | ||
** Click 'OK' to create the Storage Pool once all of the Storage pool settings are configured correctly. | ** Click 'OK' to create the Storage Pool once all of the Storage pool settings are configured correctly. | ||
| + | [[File:Qs_ha_create_storage_pool.png|600px]] | ||
=== Back-end Disk/LUN Connectivity Checklist === | === Back-end Disk/LUN Connectivity Checklist === | ||
| − | + | Following pool creation, return to the Physical Disks view and verify that the storage pool disks show the Storage Pool name for all disks on both nodes. | |
| + | [[File:Qs_ha_verify_disks_shared_withpool.png|1000px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | <!-- Possibly move this to a troubleshooting section at the bottom of the document later --> | ||
| + | If you don't see the storage pool name label on the pool's disk devices on both appliances use this checklist to verify possible connection or configuration problems. | ||
* Make sure there is connectivity from both QuantaStor appliances used in the Site Cluster to the back-end shared JBOD for the storage pool or the back-end SAN. | * Make sure there is connectivity from both QuantaStor appliances used in the Site Cluster to the back-end shared JBOD for the storage pool or the back-end SAN. | ||
* Verify FC/SAS cables are securely seated and link activity lights are active (FC). | * Verify FC/SAS cables are securely seated and link activity lights are active (FC). | ||
| Line 217: | Line 233: | ||
* Cluster-in-a-Box solutions provide these hardware requirements in a single HA QuantaStor Appliance and are recommended for small configurations (less than 25x drives) | * Cluster-in-a-Box solutions provide these hardware requirements in a single HA QuantaStor Appliance and are recommended for small configurations (less than 25x drives) | ||
| − | == Storage Pool High-Availability Group | + | == Storage Pool High-Availability Group Configuration == |
| + | <!-- Adjusted title to in-line with other sections and clarify this is creation/setup and not manage-existing scenario --> | ||
| − | Now that the Site Cluster has been created (including the two appliances that will be used in the cluster) and the Storage Pool has been created to be made HA, the final steps are to create a ''Storage Pool HA Group'' for the pool and then to make a ''Storage Pool HA Virtual IP (VIF)'' in the HA group. If you have not setup a Site Cluster with two cluster/heartbeat rings for redundancy please go to the [[Clustered_HA_SAN/NAS_(ZFS_based)_Storage_Pool_Setup# | + | Now that the Site Cluster has been created (including the two appliances that will be used in the cluster) and the Storage Pool has been created to be made HA, the final steps are to create a ''Storage Pool HA Group'' for the pool and then to make a ''Storage Pool HA Virtual IP (VIF)'' in the HA group. If you have not setup a Site Cluster with two cluster/heartbeat rings for redundancy please go to the [[Clustered_HA_SAN/NAS_(ZFS_based)_Storage_Pool_Setup#Site_Cluster_Configuration|previous section]] and set that up first. |
| + | <!-- Adjusted link for adjusted section title --> | ||
=== Creating the Storage Pool HA Group === | === Creating the Storage Pool HA Group === | ||
| − | The Storage Pool HA Group is an administrative object in the grid which associates one or more virtual IPs with a HA | + | The Storage Pool HA Group is an administrative object in the grid which associates one or more virtual IPs with a HA Storage Pool and is used to take actions such as enabling/disabling automatic fail-over, and execution of manually activated fail-over operations. Storage Pool HA Group creation be performed via a number of short cuts: |
| + | * Under the Storage Management tool window, expand the Storage Pool drawer, right click and select ''Create High Availability Group'' | ||
| + | * Under the Storage Management tool window, expand the Storage Pool drawer and click the ''Create Group'' button under ''Storage Pool HA Group'' in the ribbon bar | ||
| + | * Under the High Availability tool window, click the ''Create Group'' button under ''Storage Pool HA Group'' in the ribbon bar | ||
| − | [[File: | + | [[File:Qs_ha_create_hagroup_ribbon.png|900px]] |
| − | + | The ''Create Storage Pool High-Availability Group'' dialog will be pre-populated with values based on your available storage pool. | |
| + | [[File:Qs_ha_create_storage_pool_ha_group_dialogue.png]] | ||
| − | + | * The name can be customized if desired, but it is best practice to make it easy to determine which Storage Pool is being managed. Description is optional. | |
| + | * Verify the intended pool is listed. | ||
| + | * Primary node will be set to the node with the storage pool currently imported. | ||
| + | * Select the Secondary node (if more than 2 nodes in the Site Cluster) | ||
| − | * Configure the IP | + | === HA Virtual Network Interface Configuration === |
| + | <!-- Expanded instructions on how to find the HA Group --> | ||
| + | HA Virtual Network Interfaces can be created clicking on the ''High Availability'' toolbar option, expanding the ''Storage Pool HA Groups' drawer and right clicking on the High Availability Group and choosing ''Create High Availability Network Interface...'' | ||
| + | <!-- IMG: create_ha_virtual_network.png --> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <!-- IMG: create_ha_virtual_network_dialog.png --> | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Configure the IP and subnet mask for the HA Group's Virtual Network interface and choose the corresponding ethernet device for that network. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <!-- Following this step, the secondary node was lost from the cluster for ~1 minute --> | ||
=== HA Group Activation === | === HA Group Activation === | ||
| − | + | Finally, the High Availability Group can be activated by right Clicking on the High Availability Group and choosing ''Activate High Availability Group...'' Activating the HA Group will tell the Cluster to begin monitoring and managing the resource. | |
| + | |||
| + | <!-- IMG hagroup-activate-dialog.png --> | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Clicking ''OK'' will change the HA Group Status to online and begin cluster management of the resource. | ||
=== Failover Scenarios === | === Failover Scenarios === | ||
| Line 243: | Line 281: | ||
The Manual Failover process will gracefully failover the Shared Storage Pool from the original node with ownership to the partner node who will take ownership of the Share Storage Pool and provide client access to the Storage Volume and/or Network Share resources. | The Manual Failover process will gracefully failover the Shared Storage Pool from the original node with ownership to the partner node who will take ownership of the Share Storage Pool and provide client access to the Storage Volume and/or Network Share resources. | ||
| − | To trigger a Manual Failover for maintenance or for testing, right | + | To trigger a Manual Failover for maintenance or for testing, right click on the High Availability Group and choose the Failover High Availability Group option. In the dialog, choose the node you would like to failover to and click 'ok' to start the manual failover. |
| + | |||
| + | <!-- IMG: execute_manual_failover_dialog.png --> | ||
==== Automatic HA Failover ==== | ==== Automatic HA Failover ==== | ||
| − | In the event that a failure is detected on the node that has ownership of the Shared Storage Pool, an Automatic HA Failover event will be triggered. This automatic event will release ownership of the Shared Storage Pool from the affected node and | + | In the event that a failure is detected on the node that has ownership of the Shared Storage Pool, an Automatic HA Failover event will be triggered. This automatic event will release ownership of the Shared Storage Pool from the affected node and its partner node will take ownership and provide client access to the Storage Volume and/or Network Share resources. |
=== Triage/Troubleshooting === | === Triage/Troubleshooting === | ||
Revision as of 17:04, 24 February 2016
Contents
- 1 Introduction
- 2 High Availability Tiered SAN/ZFS based SAN/NAS Storage Layout
- 3 High Availability Shared JBOD/ZFS based SAN/NAS Storage Layout
- 4 Site Cluster Configuration
- 5 Cluster HA Storage Pool Creation
- 6 Storage Pool High-Availability Group Configuration
Introduction
QuantaStor's clustered storage pool configurations ensure high-availability (HA) in the event of a node outage or storage connectivity to the active node is lost. From a hardware perspective a QuantaStor deployment of one or more clustered storage pools requires at least two QuantaStor appliances so that automatic fail-over can occur in the event that the active appliance goes offline. Another requirement of these configurations is that the disk storage devices for the highly-available pool cannot be in either of the server units. Rather the storage must come from an external source which can be as simple as using one or more SAS JBOD enclosures or for higher performance configurations could be a SAN delivering block storage (LUNs) to the QuantaStor front-end appliances over FC (preferred) or iSCSI. The following two sections outline the minimum hardware requirements for each.
Setup and Configuration Overview
- Install both QuantaStor Appliances with the most recent release of QuantaStor.
- Apply the QuantaStor Gold, Platinum or Cloud Edition license key to each appliance. Each key must be unique.
- Create a Grid and join both QuantaStor Appliances to the grid.
- Configure SAS Hardware and Verify connectivity of SAS cables from HBAs to JBOD
- LSI SAS HBA's must be configured with the 'Boot Support' MPT BIOS option configured to 'OS only' mode.
- Verify that the SAS disks installed in both systems appear to both head nodes in the WebUI Hardware Enclosures and Controllers section.
- Create Network and Cluster heartbeat configuration and Verify network connectivity
- At least two NICs are required for a HA Cluster configuration with separate networks
- Create a Storage Pool
- Use only drives from shared storage
- Create Storage Pool HA Group
- Create one or more Storage Pool HA Virtual Interfaces
- Activate the Storage Pool
- Test failover
High Availability Tiered SAN/ZFS based SAN/NAS Storage Layout
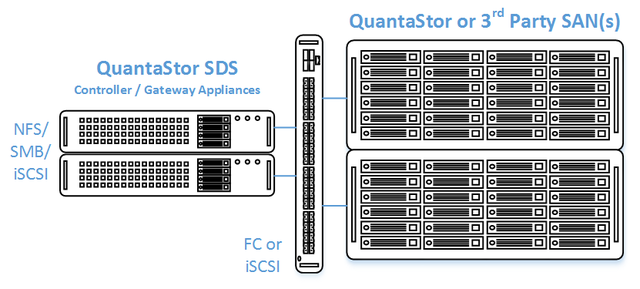
In this configuration the QuantaStor front-end controller appliances are acting as a gateway to the storage in the SANs on the back-end. QuantaStor has been tested with NetApp and HP MSA 3rd party SANs as back-end storage as well as with QuantaStor SDS as a back-end SAN. Please contact support@osnexus.com for the latest HCL for 3rd party SAN support or to get additional SAN support added to the HCL.
Minimum Hardware Requirements
- 2x (or more) QuantaStor appliances which will be configured as front-end controller nodes
- 2x (or more) QuantaStor appliance configured as back-end data nodes with SAS or SATA disk
- High-performance SAN (FC/iSCSI) connectivity between front-end controller nodes and back-end data nodes
Setup Process
All Appliances
- Login to the QuantaStor web management interface on each appliance
- Add your license keys, one unique key for each appliance
- Setup static IP addresses on each appliance (DHCP is the default and should only be used to get the appliance initially setup)
- Right-click on the storage system and set the DNS IP address (eg 8.8.8.8), and your NTP server IP address
Back-end Appliances (Data Nodes)
- Setup each back-end data node appliance as per basic appliance configuration with one or more storage pools, each with one storage volume per pool.
- Ideal pool size is 10 to 20 drives, you may need to create multiple pools per back-end appliance.
- SAS is recommended but enterprise SATA drives can also be used
- HBA(s) or Hardware RAID controller(s) can be used for storage connectivity
Front-end Appliances (Controller Nodes)
- Connectivity between the front-end and back-end nodes can be FC or iSCSI
FC SAN Back-end Configuration
- Create Host entries, one for each front-end appliance and add the WWPN of each of the FC ports on the front-end appliances which will be used for intercommunication between the front-end and back-end nodes.
- Direct point-to-point physical cabling connections can be made in smaller configurations to avoid the cost of an FC switch. Here's a guide that can help with some advice on FC zone setup for larger configurations using a back-end fabric.
- If you're using a FC switch you should use a fabric topology that will give you fault tolerance.
- Back-end appliances must use Qlogic QLE 8Gb or 16Gb FC cards as QuantaStor can only present Storage Volumes as FC target LUNs via Qlogic cards.
iSCSI SAN Back-end Configuration
- It is highly recommended to separate the networks for the front-end (client communication) vs back-end (communicate between the control and data appliances).
- For iSCSI connectivity to the back-end nodes, create a Software iSCSI Adapter by going to the Hardware Controllers & Enclosures section and adding a iSCSI Adapter. This will take care of logging into and accessing the back-end storage. The back-end storage appliances must assign their Storage Volumes to all the Hosts for the front-end nodes with their associated iSCSI IQNs.
- Right-click to Modify Network Port of each port you want to disable client iSCSI access on. If you have 10GbE be sure to disable iSCSI access on the slower 1GbE ports used for management access and/or remote-replication.
HA Network Setup
- Make sure that eth0 is on the same network on both appliances
- Make sure that eth1 is on the same but separate network from eth0 on both appliances
- Create the Site Cluster with Ring 1 on the first network and Ring 2 on the second network, both front-end nodes should be in the Site Cluster, back-end nodes can be left out. This establishes a redundant (dual ring) heartbeat between the front-end appliances which will be used to detect hardware problems which in turn will trigger a failover of the pool to the passive node.
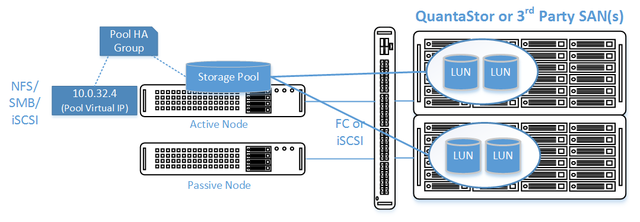
HA Storage Pool Setup
- Create a Storage Pool on the first front-end appliance (ZFS based) using the physical disks which have arrived from the back-end appliances.
- QuantaStor will automatically analyze the disks from the back-end appliances and stripe across the appliances to ensure proper fault-tolerance across the back-end nodes.
- Create a Storage Pool HA Group for the pool created in the previous step. If the storage is not accessible to both appliances, it will block you from creating the group.
- Create a Storage Pool Virtual Interface for the Storage Pool HA Group. All NFS/iSCSI access to the pool must be through the Virtual Interface IP address to ensure highly-available access to the storage for the clients.
- Enable the Storage Pool HA Group. Automatic Storage Pool fail-over to the passive node will now occur if the active node is disabled or heartbeat between the nodes is lost.
- Test pool failover, right-click on the Storage Pool HA Group and choose 'Manual Failover' to fail-over the pool to another node.
Standard Storage Provisioning
- Create one or more Network Shares (CIFS/NFS) and Storage Volumes (iSCSI/FC)
- Create one or more Host entries with the iSCSI initiator IQN or FC WWPN of your client hosts/servers that will be accessing block storage.
- Assign Storage Volumes to client Host entries created in the previous step to enable iSCSI/FC access to Storage Volumes.
Diagram of Completed Configuration
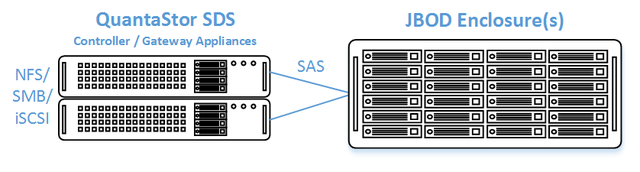
Minimum Hardware Requirements
- 2x QuantaStor storage appliances acting as storage pool controllers
- 1x (or more) SAS JBOD connected to both storage appliances
- 2x to 100x SAS HDDs and/or SAS SSDs for pool storage, all data drives must be placed in the external shared JBOD. Drives must be SAS that support Multi-port and SCSI3 Reservations, SATA drives are not supported.
- 1x hardware RAID controller (for mirrored boot drives used for QuantaStor OS operating system)
- 2x 500GB HDDs (mirrored boot drives for QuantaStor SDS operating system)
- Boot drives should be 100GB to 1TB in size, both enterprise HDDs and DC grade SSD are suitable
Storage Bridge Bay Support
Using a cluster-in-a-box or SBB (Storage Bridge Bay) system one can setup QuantaStor in a highly-available cluster configuration in a single 2U rack-mount unit. SBB units contain two hot-swap servers and a JBOD all-in-one and QuantaStor supports all SuperMicro based SBB units. For more information on hardware options and SBB please contact your OSNEXUS reseller or our solution engineering team at sdr@osnexus.com.
Setup Process
All Appliances
- Login to the QuantaStor web management interface on each appliance
- Add your license keys, one unique key for each appliance
- Setup static IP addresses on each node (DHCP is the default and should only be used to get the appliance initially setup)
- Right-click to Modify Network Port of each port you want to disable iSCSI access on. If you have 10GbE be sure to disable iSCSI access on the slower 1GbE ports used for management access and/or remote-replication.
Heartbeat/Cluster Network Configuration
- Right-click on the storage system and set the DNS IP address (eg 8.8.8.8), and your NTP server IP address
- Make sure that eth0 is on the same network on both appliances
- Make sure that eth1 is on the same but separate network from eth0 on both appliances
- Create the Site Cluster with Ring 1 on the first network and Ring 2 on the second network. This establishes a redundant (dual ring) heartbeat between the appliances.
HA Storage Pool Creation Setup
- Create a Storage Pool (ZFS based) on the first appliance using only disk drives that are in the external shared JBOD
- Create a Storage Pool HA Group for the pool created in the previous step, if the storage is not accessible to both appliances it will block you from creating the group.
- Create a Storage Pool Virtual Interface for the Storage Pool HA Group. All NFS/iSCSI access to the pool must be through the Virtual Interface IP address to ensure highly-available access to the storage for the clients. This ensures that connectivity is maintained in the event of fail-over to the other node.
- Enable the Storage Pool HA Group. Automatic Storage Pool fail-over to the passive node will now occur if the active node is disabled or heartbeat between the nodes is lost.
- Test pool fail-over, right-click on the Storage Pool HA Group and choose 'Manual Fail-over' to fail-over the pool to another node.
Storage Provisioning
- Create one or more Network Shares (CIFS/NFS) and Storage Volumes (iSCSI/FC)
- Create one or more Host entries with the iSCSI initiator IQN or FC WWPN of your client hosts/servers that will be accessing block storage.
- Assign Storage Volumes to client Host entries created in the previous step to enable iSCSI/FC access to Storage Volumes.
Diagram of Completed Configuration
Site Cluster Configuration
The Site Cluster represents a group of two or more appliances that have an active heartbeat mechanism which is used to activate resource fail-over in the event that a resource (storage pool) goes offline. Site Clusters should be comprised of QuantaStor appliances which are all in the same location but could span buildings within the same site. The heartbeat expects a low latency connection and is typically done via dual direct Ethernet cable connections between a pair of QuantaStor appliances but could also be done with Ethernet switches in-between.
Grid Setup
Both appliances must be in the same grid before the Site Cluster can be created. Grid creation takes less than a minute and the buttons to create the grid and add a second node to the grid are in the ribbon bar. QuantaStor appliances can only be members of a single grid at a time but up to 64 appliances can be added to a grid which can contain multiple independent Site Clusters.
Site Cluster Network Configuration
Before beginning, note that when you create the Site Cluster it will automatically create the first heartbeat ring (Cluster Ring) on the network that you have specified. This can be a direct connect private network between two appliances or the ports could be connected to a switch. The key requirement is that the name of the ports used for the Cluster Ring must be the same. For example, if eth0 is the port on Appliance A with IP 10.3.0.5/16 then you must configure the matching eth0 network port on Appliance B with an IP on the same network (10.3.0.0/16), for example 10.3.0.7/16.
- Each Highly Available Virtual Network Interface requires Three IP Addresses be configured in the same subnet: one for the Virtual Network Interface and one for each Network Device on each QuantaStor Storage Appliance.
- Both QuantaStor Appliances must have unique IP address for their Network devices.
- Each Management and Data network must be on separate subnets to allow for proper routing of requests from clients and proper failover in the event of a network failure.
To change the configuration of the network ports to meet the above requirements please see the section on Network Port Configuration.
Heartbeat Networks must be Dedicated
The network subnet used for heartbeat activity should not be used for any other purpose besides the heartbeat. Using the above example, the network of 10.3.x.x/16 and 10.4.x.x/16 are being used for the heartbeat traffic. Traffic for client communication such as NFS/iSCSI traffic to the appliance via the storage pool virtual IP (see next section) must be on a separate network, for example, 10.111.x.x/16. Mixing the HA heartbeat traffic with the client communication traffic can cause a false-positive failover event to occur.
Creating the Site Cluster
The Site Cluster name is a required field and can be set to anything you like, for example ha-pool-cluster. The location and description fiels are optional. Note that all of the network ports selected are on the same subnet with unique IPs for each node. These are the IP addresses that will be used for heartbeat communication. Client communication will be handled later in the Creating a Virtual IP in the Storage Pool HA Group section.
Dual Heartbeat Rings Required
Any cluster intended for production deployment must have at least two heartbeat Cluster Rings configured. Configurations using a single heartbeat Cluster Ring are fragile and are only suitable for test configurations not intended for production use. Without dual rings in place, it is very easy for a false positive failover event to occur, making any network changes likely to activate a fail-over inadvertently.
After creating the Site Cluster, an initial Cluster Ring will exist. Proceed by creating a second one by choosing 'Add Cluster Ring' from the toolbar.
Cluster HA Storage Pool Creation
Creation of a HA storage pool is the same as the process for creating a non-HA storage pool. The pool should be created on the appliance that will be acting as the primary node for the pool but that is not required. As of QuantaStor v3.17, encrypted HA storage pools can be created.
Disk Connectivity Pre-checks
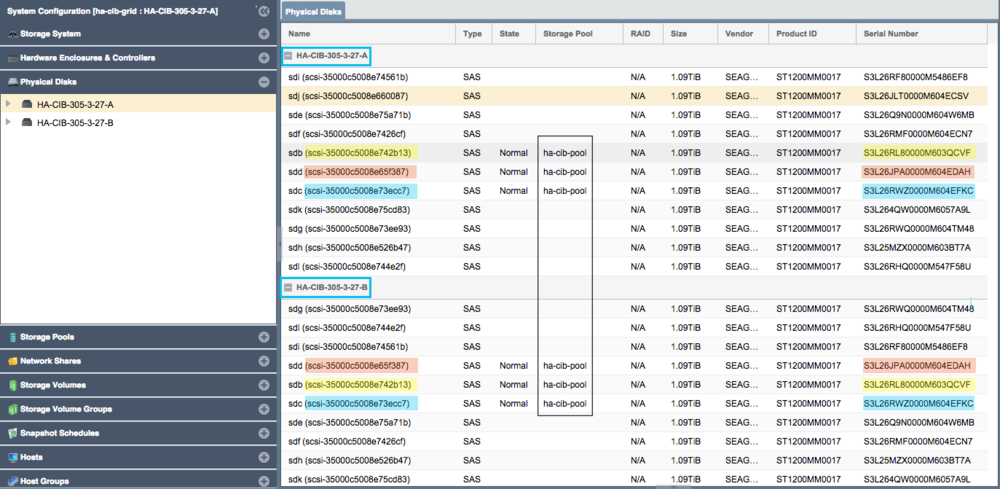
Any storage Storage Pool which is to be made Highly-Available must be configured such that both appliances used in the HA configuration both have access to all disks used by the storage pool. This necessarily requires that all devices used by a storage pool (including cache, log, and hot-spare devices) must be in a shared external JBOD or SAN. Verify connectivity to the back-end storage used by the Storage Pool via the Physical Disks section.
- Note how devices with the same ID/Serial Numbers are visible on both storage appliances. This is a strict requirement for creating Storage Pool HA Groups.
- Dual-ported SAS drives must be used when deploying a HA configuration with a JBOD backend.
- Enterprise and Data Center (DC) grade SATA drives can be used in a Tiered SAN HA configuration with QuantaStor appliances used as back-end storage rather than a JBOD.
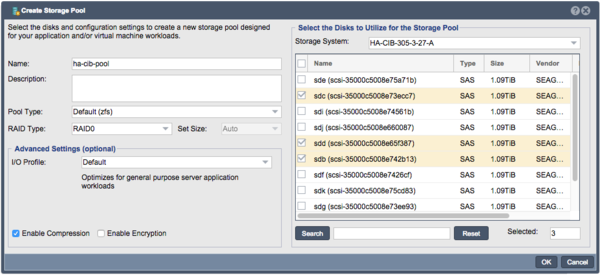
Storage Pool Creation (ZFS)
Once the disks have been verified as visible to both nodes in the cluster, proceed with Storage Pool creation using the following steps:
- Configure the Storage Pool on one of the nodes using the Create Storage Pool dialog.
- Provide a Name for the Storage Pool
- Choose the Pool Type of Default (zfs)
- Choose the RAID Type and I/O profile that will suit your use case best, more details are available in the Soultion Design Guide.
- Select the shared storage disks that you would like to use that will suit your RAID type and that were previosuly confirmed to be accessible to both QuantaStor Appliances.
- Click 'OK' to create the Storage Pool once all of the Storage pool settings are configured correctly.
Back-end Disk/LUN Connectivity Checklist
Following pool creation, return to the Physical Disks view and verify that the storage pool disks show the Storage Pool name for all disks on both nodes.
If you don't see the storage pool name label on the pool's disk devices on both appliances use this checklist to verify possible connection or configuration problems.
- Make sure there is connectivity from both QuantaStor appliances used in the Site Cluster to the back-end shared JBOD for the storage pool or the back-end SAN.
- Verify FC/SAS cables are securely seated and link activity lights are active (FC).
- All drives used to create the storage pool must be SAS, FC, or iSCSI devices that support multi-port and SCSI3 Persistent Reservations.
- SAS JBOD should have at least two SAS Expansion ports. Having a JBOD with 3 or more expansions ports and Redundant SAS Expander/Environment Service Modules(ESM) is prefferred.
- SAS JBOD cables should be within standard SAS cable lengths (less than 15 meters) of the SAS HBA's installed in the QuantaStor appliances.
- Faster devices such as SSDs and 15K RPM platter disk should be placed in a separate enclosure from the NL-SAS disks to ensure best performance.
- Cluster-in-a-Box solutions provide these hardware requirements in a single HA QuantaStor Appliance and are recommended for small configurations (less than 25x drives)
Storage Pool High-Availability Group Configuration
Now that the Site Cluster has been created (including the two appliances that will be used in the cluster) and the Storage Pool has been created to be made HA, the final steps are to create a Storage Pool HA Group for the pool and then to make a Storage Pool HA Virtual IP (VIF) in the HA group. If you have not setup a Site Cluster with two cluster/heartbeat rings for redundancy please go to the previous section and set that up first.
Creating the Storage Pool HA Group
The Storage Pool HA Group is an administrative object in the grid which associates one or more virtual IPs with a HA Storage Pool and is used to take actions such as enabling/disabling automatic fail-over, and execution of manually activated fail-over operations. Storage Pool HA Group creation be performed via a number of short cuts:
- Under the Storage Management tool window, expand the Storage Pool drawer, right click and select Create High Availability Group
- Under the Storage Management tool window, expand the Storage Pool drawer and click the Create Group button under Storage Pool HA Group in the ribbon bar
- Under the High Availability tool window, click the Create Group button under Storage Pool HA Group in the ribbon bar
The Create Storage Pool High-Availability Group dialog will be pre-populated with values based on your available storage pool.
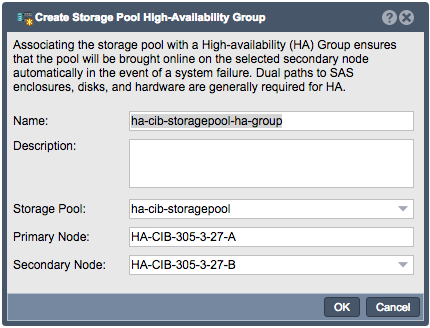
- The name can be customized if desired, but it is best practice to make it easy to determine which Storage Pool is being managed. Description is optional.
- Verify the intended pool is listed.
- Primary node will be set to the node with the storage pool currently imported.
- Select the Secondary node (if more than 2 nodes in the Site Cluster)
HA Virtual Network Interface Configuration
HA Virtual Network Interfaces can be created clicking on the High Availability toolbar option, expanding the Storage Pool HA Groups' drawer and right clicking on the High Availability Group and choosing Create High Availability Network Interface...
- Configure the IP and subnet mask for the HA Group's Virtual Network interface and choose the corresponding ethernet device for that network.
HA Group Activation
Finally, the High Availability Group can be activated by right Clicking on the High Availability Group and choosing Activate High Availability Group... Activating the HA Group will tell the Cluster to begin monitoring and managing the resource.
- Clicking OK will change the HA Group Status to online and begin cluster management of the resource.
Failover Scenarios
Manual HA Failover Steps / Testing Failover
The Manual Failover process will gracefully failover the Shared Storage Pool from the original node with ownership to the partner node who will take ownership of the Share Storage Pool and provide client access to the Storage Volume and/or Network Share resources.
To trigger a Manual Failover for maintenance or for testing, right click on the High Availability Group and choose the Failover High Availability Group option. In the dialog, choose the node you would like to failover to and click 'ok' to start the manual failover.
Automatic HA Failover
In the event that a failure is detected on the node that has ownership of the Shared Storage Pool, an Automatic HA Failover event will be triggered. This automatic event will release ownership of the Shared Storage Pool from the affected node and its partner node will take ownership and provide client access to the Storage Volume and/or Network Share resources.
Triage/Troubleshooting
qs-iofence
The qs-iofence devstatus utility is helpful for the diagnosis and troubleshooting of SCSI reservations on disks used by HA Storage Pools.
qs-util devicemap
The qs-util devicemap utility is helpful for checking via the CLI what disks are present on the system.