Difference between revisions of "Create Storage Pool"
m |
m (→Selecting the RAID Type) |
||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
=== Selecting the RAID Type === | === Selecting the RAID Type === | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
=== Selecting Disks === | === Selecting Disks === | ||
Revision as of 19:22, 6 November 2017
A storage pool is a combination of one or more disks combined together into a flexible abstract layer from which you can provision both storage volumes (LUNs) and network shares. Storage pools have support for software RAID levels including RAID0, RAID1/10, RAID5/50/Z1, RAID6/60/Z2, and RAIDZ3. QuantaStor storage pools default to using the ZFS filesystem and have the added advantage that you can expand them by adding more storage to them at any time. Note that one cannot shrink storage pools it is important to take care when expanding a given pool.
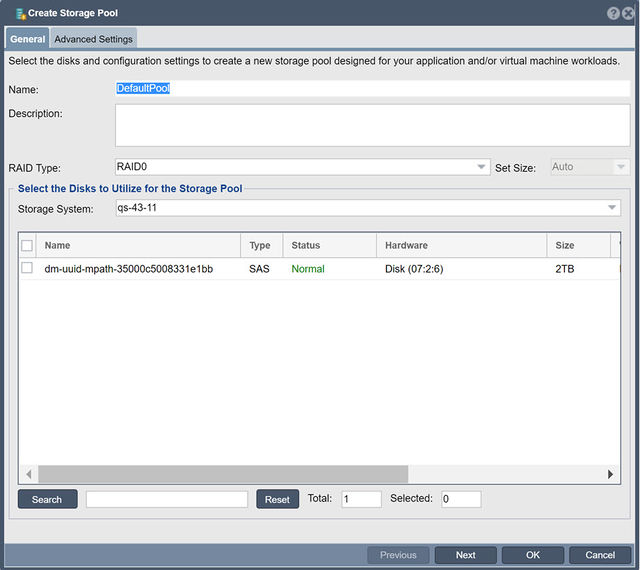
Selecting the RAID Type
Selecting Disks
If you're selecting multiple disks be sure to select disks of the same size. If you combine disks of different sizes then the lowest common denominator will be used. For example, if you have 4 disks of differing sizes such as 1TB, 2TB, 3TB and 4TB combined together using RAID0, you will have only 4TB usable. The same disks combined using RAID5 would have only 3TB usable.
It is also recommended that you use disks all from the same manufacturer rather than mixing drives which may have different performance characteristics.
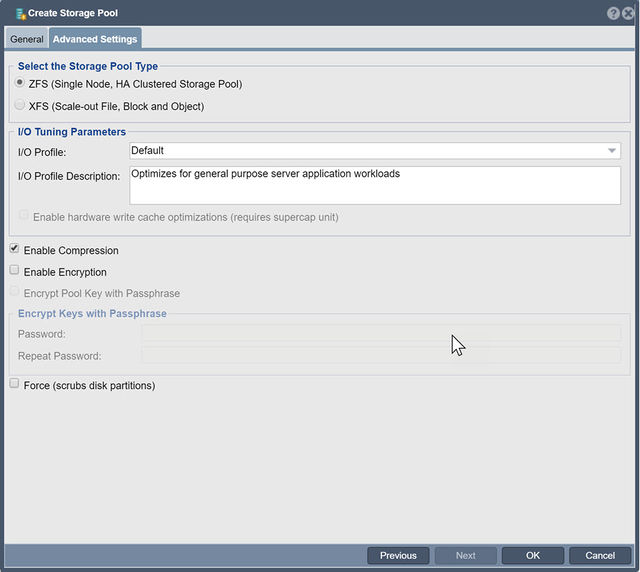
Selecting an I/O Profile
IO profiles allow you to adjust some settings like block size and read-ahead amounts for the storage pool to tune the pool for specific workloads.
Write Cache Optimizations
Enable this if you have a hardware RAID controller with a flash cache or battery backup unit which protects the write cache in the controller.
Compression
Only the ZFS storage pool type supports compression. In general compression uses very little CPU power and will boost performance as it can greatly reduce the amount of data written and read from disk. Typical performance increases from enabling compression is 10%.
Search/Reset Buttons
You may refine the Volumes displayed by entering search criteria and pressing Search button to reduce the volumes displayed. Multiple comma separated values may be used to further refine the volumes displayed. To see all the volumes press the Reset button.
Interpreting Hardware Information
For disks attached to some HBA cards, the "Hardware" column contains information about the Hardware Disk physical location, in the form of "(<HBA-PCI-Addr>:<Enclosure-Number>:<Slot-Number>)". For example:"3:8:12", or "81:252:11". The administrator can sort the disk table on this field, and using this information can make an informed selection of disks based on requirements for colocation, redundancy, etc.