Create Storage Pool High-Availability Group
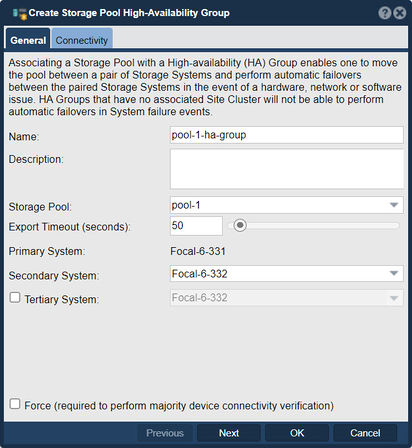
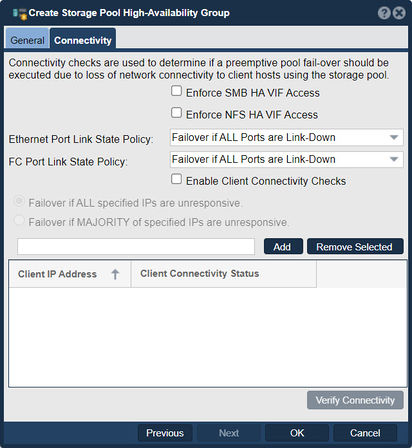
This feature allows you to combine multiple storage pools into a high-availability configuration, enhancing data redundancy, fault tolerance, and system resilience. Select an HA group to use as a failover.
The key purposes and benefits of creating a Storage Pool High-Availability Group in QuantaStor:
- High Availability: By creating a high-availability group, you can ensure continuous availability of storage resources even in the event of failures. The group consists of multiple storage pools that are configured for redundancy and failover. If one storage pool becomes unavailable or experiences issues, the data and services can automatically fail over to another pool within the group, minimizing downtime and maintaining access to stored data.
- Data Redundancy: Each storage pool within the high-availability group can be configured with data redundancy mechanisms like RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks). RAID provides redundancy by distributing data across multiple drives, allowing for data reconstruction and recovery in the event of drive failures. By combining storage pools with RAID configurations, the high-availability group ensures that data remains protected and accessible even when individual drives or pools experience issues.
- Load Balancing: The high-availability group can be configured to distribute storage loads across multiple storage pools. This load balancing mechanism helps optimize performance and resource utilization by evenly distributing I/O operations and workloads across the available pools. It ensures that no single pool becomes overloaded, enhancing overall system performance.
- Failover and Recovery: In the event of a failure or issue with a storage pool, the high-availability group provides failover capabilities. Data and services can be automatically redirected to a standby pool within the group, ensuring uninterrupted access to stored data. The failover and recovery process is typically automated, reducing the need for manual intervention and minimizing downtime.
- Simplified Management: QuantaStor provides a centralized management interface for configuring and managing the high-availability group. You can monitor the health and status of individual storage pools within the group, perform maintenance tasks, and initiate failover or recovery operations. This simplifies the administration of high-availability configurations and enhances overall system management.
- Scalability: The high-availability group can accommodate the addition of new storage pools as the storage requirements grow. You can expand the group by adding more pools to increase the storage capacity and redundancy. This scalability feature allows for seamless growth and adaptability to changing storage needs.
Overall, the "Create Storage Pool High-Availability Group" feature in QuantaStor enables the creation of a group of storage pools with high availability capabilities. It enhances data redundancy, fault tolerance, and system resilience by combining multiple pools with redundancy mechanisms, load balancing, failover, and recovery capabilities. This feature ensures continuous availability of storage resources, minimizes downtime, and simplifies the management of high-availability configurations.
Navigation: Storage Management --> Storage Pools --> Storage Pool HA Resource Group --> Create Group (toolbar)
or
Navigation: Cluster Resource Management --> Storage Pool HA Groups --> Storage Pool HA Resource Group --> Create Group (toolbar)