Difference between revisions of "Replication Schedule Activate Checkpoints"
(Created page with "Select the volumes and shares to be marked as Active Checkpoints, the schedule will also be set to disabled. Aliases provide access to the checkpoints via the source share nam...") |
m |
||
| (6 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | [[File:Activate Checkpts.jpg|512px|thumb|Select the volumes and shares to be marked as Active Checkpoints, the schedule will also be set to disabled.]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | The "Activate Checkpoints for Replication Schedule" feature in QuantaStor serves the purpose of enabling administrators to create and manage checkpoints for replication schedules. Checkpoints, also known as snapshots or point-in-time copies, capture the state of a volume or file system at a specific moment in time. | ||
| + | |||
Select the volumes and shares to be marked as Active Checkpoints, the schedule will also be set to disabled. Aliases provide access to the checkpoints via the source share name for easy fail-over of services. | Select the volumes and shares to be marked as Active Checkpoints, the schedule will also be set to disabled. Aliases provide access to the checkpoints via the source share name for easy fail-over of services. | ||
| − | ' | + | By creating checkpoints, you can establish recovery points along the replication timeline. These checkpoints can be used to restore the destination volume to a specific state, effectively rolling back the replicated data to a previous version. |
| + | |||
| + | Here's the purpose of activating checkpoints for a replication schedule: | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Data Consistency: Checkpoints ensure data consistency by capturing a consistent view of the source volume or file system at the time of replication. When a replication schedule is initiated, a checkpoint is created to provide a reference point for data replication. This ensures that replicated data reflects a consistent state and is not affected by ongoing changes to the source volume. | ||
| + | *Point-in-Time Recovery: Checkpoints enable point-in-time recovery for replicated data. If data corruption or data loss occurs in the source volume, administrators can use checkpoints to restore the volume to a previous state, effectively rolling back changes to the point of the checkpoint. This helps mitigate the impact of data corruption or accidental deletions. | ||
| + | *Replication Efficiency: Checkpoints improve replication efficiency by reducing the amount of data transferred during replication. Instead of transferring the entire volume or file system each time replication occurs, only the changes made since the last checkpoint need to be replicated. This minimizes network bandwidth usage and accelerates replication performance. | ||
| + | *Granular Recovery: Checkpoints provide administrators with granular recovery options by allowing them to choose specific checkpoints for recovery. Administrators can select checkpoints corresponding to specific points in time to restore data to a desired state, providing flexibility in data recovery operations. | ||
| + | *Data Integrity Verification: Checkpoints serve as reference points for verifying data integrity during replication. Administrators can compare the contents of checkpoints on the source and destination volumes to ensure that replicated data matches the original data and has not been corrupted or tampered with during the replication process. | ||
| + | *Disaster Recovery Preparedness: Checkpoints enhance disaster recovery preparedness by providing administrators with multiple recovery points to choose from. In the event of a disaster or data loss, administrators can leverage checkpoints to restore data to a known good state, minimizing downtime and data loss. | ||
| + | Overall, the purpose of activating checkpoints for a replication schedule in QuantaStor is to enhance data consistency, recovery capabilities, replication efficiency, and disaster recovery preparedness for replicated data. By leveraging checkpoints, administrators can ensure data integrity, streamline replication operations, and mitigate the impact of data loss or corruption in the storage environment. | ||
| − | |||
| + | '''Navigation:''' Remote Replication --> Volume & Share Replication Schedules --> Replication Schedule --> Activate Checkpoints ''(toolbar)'' | ||
| + | <br><br> | ||
{{Template:ReturnToWebGuide}} | {{Template:ReturnToWebGuide}} | ||
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:QuantaStor6]] |
[[Category:WebUI Dialog]] | [[Category:WebUI Dialog]] | ||
[[Category:Requires Review]] | [[Category:Requires Review]] | ||
Latest revision as of 15:07, 29 April 2024
The "Activate Checkpoints for Replication Schedule" feature in QuantaStor serves the purpose of enabling administrators to create and manage checkpoints for replication schedules. Checkpoints, also known as snapshots or point-in-time copies, capture the state of a volume or file system at a specific moment in time.
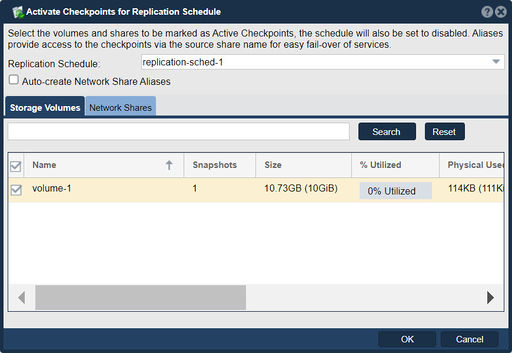
Select the volumes and shares to be marked as Active Checkpoints, the schedule will also be set to disabled. Aliases provide access to the checkpoints via the source share name for easy fail-over of services.
By creating checkpoints, you can establish recovery points along the replication timeline. These checkpoints can be used to restore the destination volume to a specific state, effectively rolling back the replicated data to a previous version.
Here's the purpose of activating checkpoints for a replication schedule:
- Data Consistency: Checkpoints ensure data consistency by capturing a consistent view of the source volume or file system at the time of replication. When a replication schedule is initiated, a checkpoint is created to provide a reference point for data replication. This ensures that replicated data reflects a consistent state and is not affected by ongoing changes to the source volume.
- Point-in-Time Recovery: Checkpoints enable point-in-time recovery for replicated data. If data corruption or data loss occurs in the source volume, administrators can use checkpoints to restore the volume to a previous state, effectively rolling back changes to the point of the checkpoint. This helps mitigate the impact of data corruption or accidental deletions.
- Replication Efficiency: Checkpoints improve replication efficiency by reducing the amount of data transferred during replication. Instead of transferring the entire volume or file system each time replication occurs, only the changes made since the last checkpoint need to be replicated. This minimizes network bandwidth usage and accelerates replication performance.
- Granular Recovery: Checkpoints provide administrators with granular recovery options by allowing them to choose specific checkpoints for recovery. Administrators can select checkpoints corresponding to specific points in time to restore data to a desired state, providing flexibility in data recovery operations.
- Data Integrity Verification: Checkpoints serve as reference points for verifying data integrity during replication. Administrators can compare the contents of checkpoints on the source and destination volumes to ensure that replicated data matches the original data and has not been corrupted or tampered with during the replication process.
- Disaster Recovery Preparedness: Checkpoints enhance disaster recovery preparedness by providing administrators with multiple recovery points to choose from. In the event of a disaster or data loss, administrators can leverage checkpoints to restore data to a known good state, minimizing downtime and data loss.
Overall, the purpose of activating checkpoints for a replication schedule in QuantaStor is to enhance data consistency, recovery capabilities, replication efficiency, and disaster recovery preparedness for replicated data. By leveraging checkpoints, administrators can ensure data integrity, streamline replication operations, and mitigate the impact of data loss or corruption in the storage environment.
Navigation: Remote Replication --> Volume & Share Replication Schedules --> Replication Schedule --> Activate Checkpoints (toolbar)