Difference between revisions of "Hardware Disk Mark Hotspare"
m |
m |
||
| (3 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
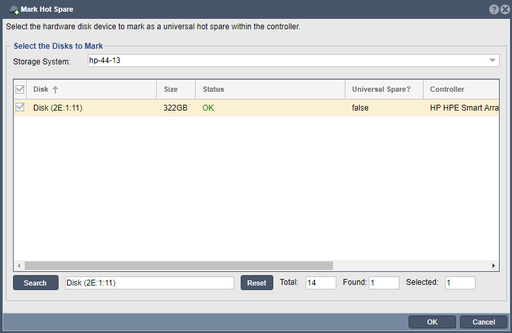
| + | [[File:mark_hwdisk_hotspare.png|512px|thumb|Mark or unMark hot-spares for RAID units.]] | ||
| + | |||
{{DISPLAYTITLE:Marking/Unmarking Hot-spares for Hardware RAID Units}} | {{DISPLAYTITLE:Marking/Unmarking Hot-spares for Hardware RAID Units}} | ||
| − | + | ||
| + | In QuantaStor, the "Mark Hot Spare" feature serves the purpose of designating a spare disk as a "hot spare" within a RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) configuration. A hot spare is a standby disk that is ready to automatically replace a failed disk within a RAID array if a failure occurs. '''Note,''' that devices marked as hot-spares within a RAID controller can only be used as a hot-spares for RAID units managed by that specific controller. As such if a system has two or more RAID controllers each one will need one or more disks marked as hot-spares in order to get automatic healing of RAID units. Systems using fault-tolerant software RAID at the Storage Pool level using HBAs have no requirement to specify hardware RAID hot-spares and in such cases this section does not apply. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The purpose of marking a disk as a hot spare includes: | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Fault Tolerance: Hot spares enhance fault tolerance within RAID configurations by providing automatic disk replacement in the event of a disk failure. When a disk failure occurs in a RAID array, the hot spare automatically takes over the failed disk's role, minimizing the risk of data loss and ensuring continuous operation of the RAID array. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Automatic Recovery: Marking a disk as a hot spare enables automatic recovery mechanisms within the RAID controller or software. In the event of a disk failure, the RAID controller or software automatically initiates the process of rebuilding the RAID array using the hot spare disk, restoring redundancy and data protection without requiring manual intervention. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Reduced Downtime: Hot spares help reduce downtime associated with disk failures by providing a rapid and automated recovery process. With a hot spare in place, the time to recover from a disk failure is minimized, allowing the RAID array to remain operational and maintain data availability during the recovery process. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Improved Reliability: By designating a spare disk as a hot spare, administrators improve the reliability and resilience of the storage infrastructure. Hot spares increase the likelihood of successful RAID array recovery in the event of a disk failure, thereby enhancing the overall reliability and availability of the storage system. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Efficient Resource Utilization: Hot spares optimize resource utilization by providing standby disks that are only activated when needed to replace failed disks. This allows organizations to maintain fault tolerance and data protection without allocating dedicated spare disks for each RAID array, resulting in more efficient use of storage resources. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Simplified Maintenance: Marking a disk as a hot spare simplifies maintenance and management tasks associated with RAID arrays. Administrators do not need to manually intervene or replace failed disks immediately upon detection of a failure, as the hot spare automatically assumes the role of the failed disk, streamlining maintenance operations and reducing administrative overhead. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Overall, the purpose of marking a disk as a hot spare in QuantaStor is to enhance fault tolerance, improve data availability, reduce downtime, and streamline maintenance operations within RAID configurations. Hot spares provide an automated and efficient mechanism for ensuring continuous operation and data protection in the event of disk failures within the storage environment. | ||
| + | |||
'''Navigation: ''' Storage Management --> Physical Disks --> (target disk) --> Mark Hot-Spare ''(rightclick)'' | '''Navigation: ''' Storage Management --> Physical Disks --> (target disk) --> Mark Hot-Spare ''(rightclick)'' | ||
| − | |||
{{Template:ReturnToWebGuide}} | {{Template:ReturnToWebGuide}} | ||
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:QuantaStor6]] |
[[Category:WebUI Dialog]] | [[Category:WebUI Dialog]] | ||
Latest revision as of 10:33, 7 April 2024
In QuantaStor, the "Mark Hot Spare" feature serves the purpose of designating a spare disk as a "hot spare" within a RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) configuration. A hot spare is a standby disk that is ready to automatically replace a failed disk within a RAID array if a failure occurs. Note, that devices marked as hot-spares within a RAID controller can only be used as a hot-spares for RAID units managed by that specific controller. As such if a system has two or more RAID controllers each one will need one or more disks marked as hot-spares in order to get automatic healing of RAID units. Systems using fault-tolerant software RAID at the Storage Pool level using HBAs have no requirement to specify hardware RAID hot-spares and in such cases this section does not apply.
The purpose of marking a disk as a hot spare includes:
- Fault Tolerance: Hot spares enhance fault tolerance within RAID configurations by providing automatic disk replacement in the event of a disk failure. When a disk failure occurs in a RAID array, the hot spare automatically takes over the failed disk's role, minimizing the risk of data loss and ensuring continuous operation of the RAID array.
- Automatic Recovery: Marking a disk as a hot spare enables automatic recovery mechanisms within the RAID controller or software. In the event of a disk failure, the RAID controller or software automatically initiates the process of rebuilding the RAID array using the hot spare disk, restoring redundancy and data protection without requiring manual intervention.
- Reduced Downtime: Hot spares help reduce downtime associated with disk failures by providing a rapid and automated recovery process. With a hot spare in place, the time to recover from a disk failure is minimized, allowing the RAID array to remain operational and maintain data availability during the recovery process.
- Improved Reliability: By designating a spare disk as a hot spare, administrators improve the reliability and resilience of the storage infrastructure. Hot spares increase the likelihood of successful RAID array recovery in the event of a disk failure, thereby enhancing the overall reliability and availability of the storage system.
- Efficient Resource Utilization: Hot spares optimize resource utilization by providing standby disks that are only activated when needed to replace failed disks. This allows organizations to maintain fault tolerance and data protection without allocating dedicated spare disks for each RAID array, resulting in more efficient use of storage resources.
- Simplified Maintenance: Marking a disk as a hot spare simplifies maintenance and management tasks associated with RAID arrays. Administrators do not need to manually intervene or replace failed disks immediately upon detection of a failure, as the hot spare automatically assumes the role of the failed disk, streamlining maintenance operations and reducing administrative overhead.
Overall, the purpose of marking a disk as a hot spare in QuantaStor is to enhance fault tolerance, improve data availability, reduce downtime, and streamline maintenance operations within RAID configurations. Hot spares provide an automated and efficient mechanism for ensuring continuous operation and data protection in the event of disk failures within the storage environment.
Navigation: Storage Management --> Physical Disks --> (target disk) --> Mark Hot-Spare (rightclick)