Join AD Domain
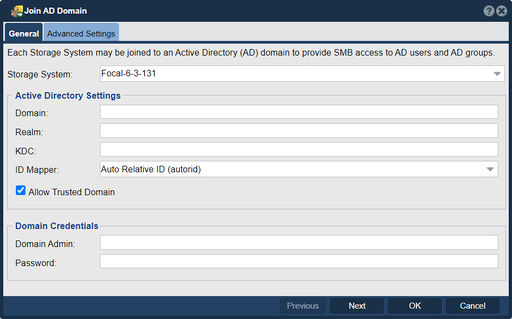
QuantaStor integrates with Microsoft Active Directory (AD) for the purposes of assigning access to Network Shares to AD users and groups. Being Linux based QuantaStor uses a service called winbind to map AD users to local Linux users and groups. This process involves mapping the Windows user IDs (SIDs) to Unix user IDs and groups (UID/GIDs) and QuantaStor provides a few options for ID mapping. By using the "Join AD Domain" feature in QuantaStor, you can accomplish the following:
- Single Sign-On (SSO): Joining the AD domain allows you to establish a trust relationship between your storage system and the domain controller. This enables users to authenticate using their existing AD credentials when accessing storage resources, eliminating the need for separate usernames and passwords. With SSO, users can seamlessly access the storage system without having to provide additional credentials.
- User and Group Management: Once the storage system is joined to the AD domain, you can leverage AD's user and group management capabilities. This means that you can easily grant or restrict access to storage resources based on AD user and group memberships. It simplifies access control and allows for consistent user management across different systems within the network.
- Enhanced Security: AD integration provides enhanced security by leveraging AD's authentication mechanisms. It ensures that only authorized users with valid AD credentials can access the storage system. Additionally, AD's security policies, such as password complexity requirements and account lockout policies, can be enforced for storage system access as well.
- Centralized Management: Joining the AD domain enables centralized management of user accounts and permissions. Instead of managing user accounts separately on the storage system, you can leverage the existing user accounts and groups defined in the AD domain. This streamlines user administration and ensures consistency across the network.
- Integration with Other Services: AD integration allows for seamless integration with other services and applications that rely on AD authentication. For example, if you have applications or services that authenticate against AD, those same credentials can be used to access the storage system. This simplifies the user experience and promotes interoperability between different systems.
Navigation: Storage Management --> Network Shares --> Active Directory --> Join AD Domain (toolbar)
ID Mapping
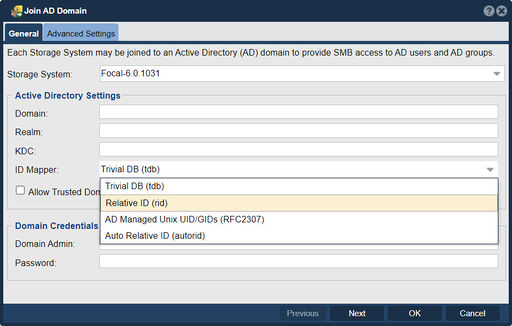
- Relative ID (RID)
RID mode is the recommended configuration for most systems as it provides a generated relative ID for each user that will generally be the same across all appliances that you deploy.
- Trivial DB (TBD)
TDB is a basic mode which allocates an ID for each user starting with 600 and going up from there. (note: edit the /etc/smb.conf file to adjust the starting offset). TDB is not recommended for configurations with more than one QuantaStor appliance as there's a high probability that the UIDs for a given AD user will be different on each appliance and this will cause problems especially when using scale-out Gluster Volumes.
- Active Directory managed Unix UID/GIDs (AD)
This is the ideal mode as all your users's UIDs and GIDs are centrally managed by your AD server. This mode does require additional configuration steps on your Windows 2008 or newer AD server.
- Auto Relative ID (autorid)
Similar to the RID mode but has the advantage of generating relative IDs for different users across multiple domains without additional ID range selection configuration steps.