Setup Guide for Clustered HA Storage Pools
Why Use a Clustered HA Storage Pool Configuration
QuantaStor's clustered storage pool configurations ensure high-availability (HA) in the event of a server outage or storage connectivity to the active node is lost. QuantaStor monitors the health of the network connections (both Ethernet & FC), the storage connectivity to the devices and disk enclosures, the health of the server, and optionally will verify ping connectivity to clients. If a problem is detected which is not a system outage (which would cause an immediate failover), the active node for a given pool will communicate with it's HA paired system to see if a fail-over to the secondary will address the issue. If so QuantaStor will preemptively failover to the secondary to restore availability to the Storage Pool. In short, high-availability technology ensures a much higher level of system up-time in the event of a server, switch, or other outage.
Requirements Before You Begin
- 2x QuantaStor servers
- 2x network interfaces per appliance for redundant cluster communication (heartbeat mechanism)
- Multipath storage connectivity from both servers to all storage media
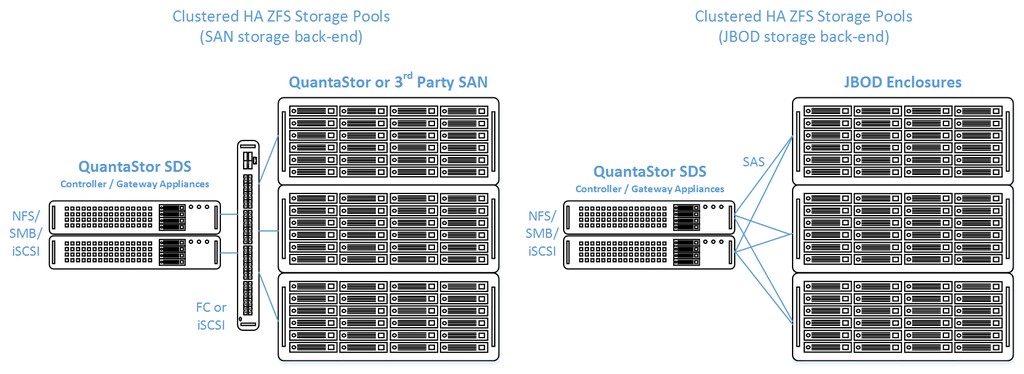
- SAS JBOD(s), NVME JBOF, FC SAN, or iSCSI SAN (must support SCSI3 Persistent Reservations or be dual-ported NVMe)
Persistent Reservations
QuantaStor's High-Availability Storage Pool solution requires that the QuantaStor appliance cluster members all have access to the Storage Pool devices so that the devices can be reserved using SCSI3-PR or NVME reserve/preempt operations. The most common way of designing these systems is with the use of 12Gb or 6Gb SAS disk enclosures capable of multipath connectivity to two or more servers.
Back-end Storage Connectivity
QuantaStor supports multiple back-end storage connection options including SAS, FC, dual-port NVMe, and iSCSI. We highly recommend using the design tools to ensure a proper design based on the scale and performance requirements for your application workloads.
External JBOD - Dual-controller Disk Expansion Units
QuantaStor supports all the major external SAS disk expansion chassis from Western Digital, Seagate, DellEMC, HPE, Supermicro and Lenovo. For the latest information on JBOD coverage please see the HA cluster design tools here.
Internal JBOD - Storage Bridge Bay Support
Storage Bridge Bay (SSB) systems can be used to create a QuantaStor HA Cluster configuration in a single 2U rack-mount unit. The SSB units, referred to as a cluster-in-a-box, contain two hot-swap servers, and a shared JBOD all in a single unit. QuantaStor supports all SuperMicro based SBB units. For more information on hardware options and SBB please contact your OSNEXUS reseller or our solution engineering team at sdr@osnexus.com.
NVMe Support
QuantaStor 5 supports dual-port NVMe based storage connectivity and has been certified for use with Western Digital Serv24HA which contains two servers and a NVMe JBOF in a single 2U chassis. More information about this configuration is available via the design tool.
Back-end SAN (FC/iSCSI) Storage via QuantaStor Servers
QuantaStor appliances can be used to provide SAN provisioned storage over Fiber-channel or iSCSI, as shown in the diagram above. Note that these systems would be separate from the HA Storage Pool cluster.
Back-end SAN (FC/iSCSI) Storage via 3rd Party SAN
Before using a 3rd Party SAN as the back-end storage for your HA cluster, please contact OSNEXUS solution design engineering via sdr@osnexus.com. Checks need to be made to ensure that the SAN properly supports the necessary SCSI3-PR commands and that the multipath configuration settings are set properly to ensure proper management of the 3rd party SAN LUNs within the QuantaStor servers.
Configuration
Setting up a new QuantaStor HA configuration takes only a few minutes and can be done entirely via the QuantaStor web management interface. If you're frequently setting up new QuantaStor systems this can also be automated using the QuantaStor CLI or REST API.
Overview
- Create the Storage Grid (see Storage Management -> Storage Systems section)
- Configure the network ports (typically eth0, eth1) with static IPs.
- Create a Storage Pool (see Storage Management -> Storage Pools section)
- Create a Site Cluster (see Cluster Resource Management -> Site Clusters section)
- Create a Storage Pool HA Group for the Storage Pool (see Storage Management -> Storage Pools section -> right-click on the pool)
- Create a Storage Pool HA VIF for the Storage Pool (see Storage Management -> Storage Pools section -> right-click on newly created HA Group)
- Test Storage Pool Fail-over (right-click on the Storage Pool, choose Execute Manual HA Failover)
Getting Started
QuantaStor should be installed on every node to be used in the cluster before beginning. For details on the installation of QuantaStor, please see the QuantaStor_Installation_Guide.
- Login to the QuantaStor web management interface on each appliance
- Add your license keys, one unique key for each appliance
- Create a Storage Grid, and add the second QuantaStor server to the Storage Grid
Networking Configuration
The high-availability system requires at least two static IP addresses per node on separate networks. QuantaStor uses DHCP to get an IP address at install time but this should be changed immediately to a static IP addresses. This is necessary when it comes time to setup the Site Cluster Heartbeat Rings.
- Expand the Storage System drawer under "Storage Management" and select the "Network Ports" tab in the center page.
- Right-click on eth0 to configure static IP information (Note, if you're logged into the Web UI via this IP you'll need to update the URL in your browser and then re-login after changing this address.)
- Right-click on eth1 to configure static IP information for the second network port (this must be on a different network than eth0)
- Right-click on the storage system and choose "Storage System Modify" on each server to set the DNS IP address (eg 8.8.8.8), and your NTP server IP address
Here's an example of what the configuration might look like. Note how eth0 and eth1 are on separate networks, this is key so that the heartbeat mechanism can ensure communication down two separate redundant paths between the systems. Note also that these ports can also be used for web management access and grid communication at the same time and do not need to be fully dedicated for the heartbeat mechanism. That said, these ports used for heartbeat are generally not used for data access at the same time if that can be avoided.
Example:
QuantaStor Server 1 - eth0=10.0.13.101 / 255.255.0.0 eth1=192.168.113.101 / 255.255.0.0 QuantaStor Server 2 - eth0=10.0.13.102 / 255.255.0.0 eth1=192.168.113.102 / 255.255.0.0
Create Storage Pool
Create a Storage Pool normally but be sure to choose a RAID10 layout for workloads that need maximum IOPS or a RAIDZ2 layout for workloads that are mostly sequential. When you press the "Auto Config" button in the Storage Pool creation dialog the system automatically analyzes the JBODs to select devices in stripe-group increments that will ensure enclosure redundancy. Using the + and - buttons will add or remove a single stripe at a time while maintaining enclosure redundancy if you have enough enclosures. For RAID10 a minimum of 2x JBODs are required with the devices evenly distributed. For RAIDZ2/60 a minimum of 3x JBODs are required with the devices evenly distributed (assuming 4d+2p). Note also that all devices in the JBOD/JBOFs must support persistent reservations. In a later step when the Storage Pool HA group is created the system will verify proper support for SCSI3-PR and will block the creation of the Storage Pool HA group if the devices are of the wrong type (examples: SATA or single port NVMe).
Create Site Cluster
The Site Cluster is a heartbeat style cluster which is comprised of two or more QuantaStor systems. Often times one will create separate clusters for each site hence the name Site Cluster. Once the Site Cluster is created in the Cluster Resource Management tab a HA group can be created on the Storage Pool and then a HA VIF added to the HA Group.
Create Storage Pool HA Group
The Storage Pool HA Group can be created by right-clicking on the Storage Pool and then choosing 'Create High-Availability Group'. The HA Group object contains the failover policy information for the pool. After the HA group is created, right-click on it and choose 'Modify HA Group..' to see and adjust the policy settings as needed.
Create Storage Pool HA Virtual Interface (VIF)
The HA VIF for the pool is an IP address which is assigned to the pool and moves with the pool when it is moved between servers. All clients connecting via iSCSI, NFS, and CIFS/SMB connectivity should be done through the HA VIF IP for a given pool to ensure that connectivity is not lost as part of the failover process.
Testing High-Availability Failover
- Before executing a HA fail-over of the pool, make sure it is operating normally. Create a Storage Volume and or a Network Share and write some data to the pool to verify connectivity. Be sure to use the HA VIF IP address when you connect to and copy files to the Network Share via NFS or SMB/CIFS from your client/initiator host.
- Review the Alerts tab to make sure that there are no items that need to be addressed. If for example the JBODs are not properly cabled to the servers an alert will be raised and visible in the Alerts tab in the web UI.
- In the Cluster Resource Management tab, make sure the Site Cluster is online and in the Healthy state. It is normal for it to be in the Warning state temporarily during the initial cluster creation and configuration process but that will resolve itself within a minute or two.
- Now you're ready to execute the Storage Pool failover, just right-click on the Storage Pool or the HA Group and choose 'Execute Manual Failover..' from the pop-up menu. This will present you with a dialog to select the other system to failover, press ok and it should failover to the other system within 30 seconds.
- Once everything is verified we recommend using the Configuration Analyzer which is in the main Storage Management section to review the network and other configuration settings on you system. This will look for network and other issues which will save time as you go through the pre-go-live checks.
- Send logs to OSNEXUS and email support@osnexus.com to request a pre-go-live check by one of our Support Engineers.