Difference between revisions of "Storage System Checklist"
From OSNEXUS Online Documentation Site
m |
m |
||
| (10 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
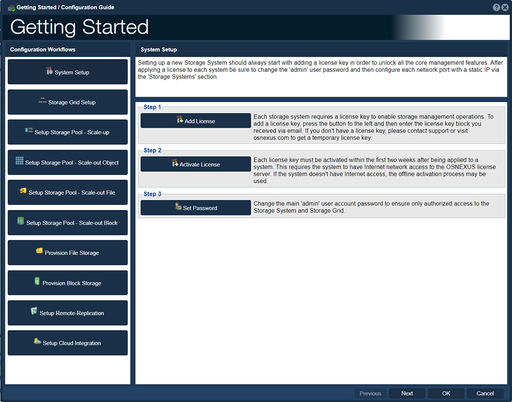
| − | The '''Getting Started | + | The '''Getting Started / Configuration Guide''' consists of a series of shortcuts to help get your QuantaStor system up and running quickly. Every step in the list is available through the normal management interface and is covered in more detail in that section. |
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|- valign="top" | |- valign="top" | ||
| − | | [[File: | + | | [[File:Getting Started.jpg|512px|none|caption|Getting Started Workflow Configuration.]] |
| | | | ||
| − | # ''' | + | # '''System Setup''' |
| − | #* | + | #* Setting up a new Storage System should always start with adding a license key in order to unlock all the core management features. After applying a license to each system be sure to change the 'admin' user password and then configure each network port with a static IP via the 'Storage Systems' section. |
| − | # ''' | + | # '''Storage Grid Setup''' |
| − | #* | + | #* Storage Grid technology makes it easy to manage large numbers of Storage Systems as one distributed system. Within a Storage Grid one can create and manage multiple scale-out and scale-up storage clusters within and across sites. |
| − | # ''' | + | # '''Setup Storage Pool - Scale-up''' |
| − | #* | + | #* Scale-up Storage Pools may be setup in single-node mode or clustered HA mode. HA Storage Pools require at least two Storage Systems and the storage media that makes up the Storage Pool must support IO fencing. Media that supports IO fencing include dual-ported SAS, dual-ported NVMe, FC, and iSCSI devices. All access to clustered HA Storage Pools is done via a clustered VIFs to ensure continuous data availability in the event the Storage Pool is moved to its paired Storage System via HA fail-over. |
| − | # ''' | + | # '''Setup Storage Pool - Scale-out Object''' |
| − | #* | + | #* Scale-out object storage configurations deliver S3 object storage via S3-compatible buckets that may also be accessed as file storage via NFS. Object storage is typically setup with an erasure-coding layout to ensure fault-tolerance and high-availability. A scale-out storage cluster using three (3) or more Storage Systems must be setup first. |
| − | # ''' | + | # '''Setup Storage Pool - Scale-out File''' |
| − | #* | + | #* Scale-out file Storage Pools are POSIX-compliant and deliver high performance NFS, SMB, and native CephFS client access. Scale-out Storage Pools are highly-available and can utilize two or more metadata service instances (MDS) to load balance and scale locking performance. |
| − | # ''' | + | # '''Setup Storage Pool - Scale-out Block''' |
| − | #* | + | #* Scale-out block Storage Pools provide highly-available block storage via the iSCSI, Fibre-Channel, and NVMeoF protocols as well as via the native Ceph RBD protocol. |
| − | # ''' | + | # '''Provision File Storage''' |
| − | #* | + | #* Network Shares may be accessed via both the NFS and the SMB file storage protocols. A Storage Pool (scale-up or scale-out) must be created before Network Shares may be provisioned. |
| − | # ''' | + | # '''Provision Block Storage''' |
| − | #* | + | #* Block storage devices are referred to as Storage Volumes. Storage Volumes may be accessed via both the iSCSI and the FC protocol on systems with the required hardware. Since Storage Volumes are provisioned from Storage Pools, a pool (ZFS or Ceph) must be created first. |
| + | # '''Setup Remote-Replication''' | ||
| + | #* Remote-replication enables one to asynchronously replicate Storage Volumes and Network Shares from any Storage Pool to a destination Storage Pool within a given Storage Grid. Replication is automated via a Replication Schedules so that it can be used as part of a business continuity and DR site fail-over plan. | ||
| + | # '''Setup Cloud Integration''' | ||
| + | #* Storage Systems can be connected to one or more major public cloud providers to provide local NAS gateway access to object storage and a means of automated backup and tiering via Backup Policies. | ||
|} | |} | ||
| Line 27: | Line 31: | ||
{{Template:ReturnToWebGuide}} | {{Template:ReturnToWebGuide}} | ||
[[Category:Incomplete]] | [[Category:Incomplete]] | ||
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:QuantaStor6]] |
[[Category:WebUI Dialog]] | [[Category:WebUI Dialog]] | ||
Latest revision as of 17:23, 13 February 2023
The Getting Started / Configuration Guide consists of a series of shortcuts to help get your QuantaStor system up and running quickly. Every step in the list is available through the normal management interface and is covered in more detail in that section.
|