Difference between revisions of "Cloud Containers / NAS Gateway"
m |
m |
||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
== NAS Gateway / Cloud Container Management == | == NAS Gateway / Cloud Container Management == | ||
| − | Cloud Containers represent a bucket that has been mapped to a Network Share within QuantaStor. When data is stored in a Cloud Container it frees up space locally on the system, however, reading data back from object services can be slow and | + | Cloud Containers represent a bucket that has been mapped to a Network Share within QuantaStor. When data is stored in a Cloud Container it frees up space locally on the system, however, reading data back from object services can be slow and can incur a fee or egress. When creating a Cloud Container on your QuantaStor system, it will appear as a Network Share, whiich can be accessed via NFS and CIFS. |
| − | + | Object services are beneficial for users who need to store data that does not require frequent access. QuantaStor can be configured to be a NAS gateway for object storage providers, including: | |
* [[Scale-out Object Setup (ceph)|QuantaStor Scale-Out Object]] | * [[Scale-out Object Setup (ceph)|QuantaStor Scale-Out Object]] | ||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
* Amazon S3 | * Amazon S3 | ||
* Microsoft Azure Blob | * Microsoft Azure Blob | ||
| − | * and other S3-compatible services | + | * and other S3-compatible services |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
A Cloud Container can only be used by one QuantaStor system at a time. If you need to add it to another system, please disable it from the first system before activating the container on another. | A Cloud Container can only be used by one QuantaStor system at a time. If you need to add it to another system, please disable it from the first system before activating the container on another. | ||
Revision as of 04:04, 20 November 2023
Contents
- 1 NAS Gateway / Cloud Container Management
- 1.1 Adding Cloud Provider Credentials
- 1.2 Creating a Cloud Container
- 1.3 Cloud Container Operations
- 1.4 Cloud Provider Support
- 1.4.1 Amazon Cloud Storage Configuration Steps
- 1.4.2 Backblaze B2 Cloud Storage Configuration Steps
- 1.4.3 Dropbox Configuration Steps
- 1.4.4 Google Cloud Storage Configuration Steps
- 1.4.5 Microsoft Azure Blob Configuration Steps
- 1.4.6 IBM Softlayer S3 Configuration Steps
- 1.4.7 Ceph Object Storage Configuration Steps
NAS Gateway / Cloud Container Management
Cloud Containers represent a bucket that has been mapped to a Network Share within QuantaStor. When data is stored in a Cloud Container it frees up space locally on the system, however, reading data back from object services can be slow and can incur a fee or egress. When creating a Cloud Container on your QuantaStor system, it will appear as a Network Share, whiich can be accessed via NFS and CIFS.
Object services are beneficial for users who need to store data that does not require frequent access. QuantaStor can be configured to be a NAS gateway for object storage providers, including:
- QuantaStor Scale-Out Object
- Seagate Lyve
- Amazon S3
- Microsoft Azure Blob
- and other S3-compatible services
A Cloud Container can only be used by one QuantaStor system at a time. If you need to add it to another system, please disable it from the first system before activating the container on another.
Adding Cloud Provider Credentials
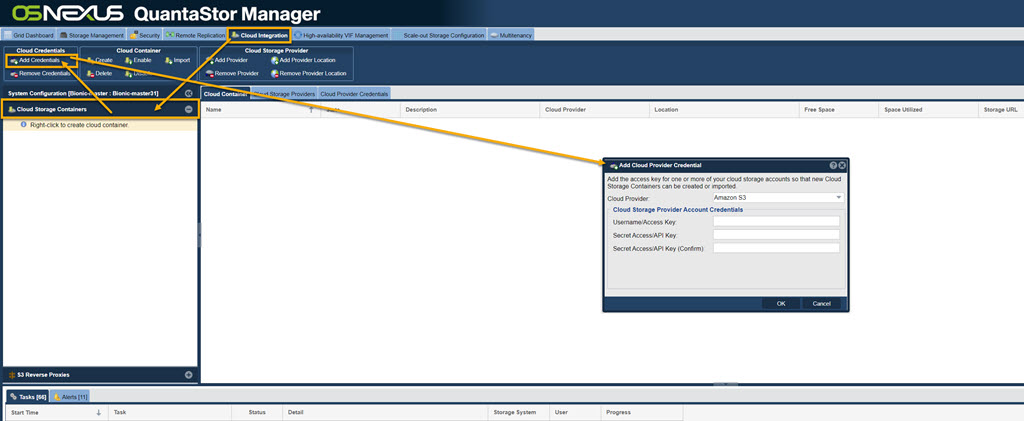
To begin using the Cloud Container feature, you will need to provide the QuantaStor system access to your Object Storage using the 'Add Cloud Provider Credentials' dialog available in the NAS Gateway tab of the WebUI as shown in the example:
The credentials for your object storage cloud can be found in the security/authentication pages of your Amazon S3,
Google Cloud Storage, or SoftLayer Cloud Storage accounts.
Once your credentials have been added you can begin creating cloud containers within QuantaStor.
Creating a Cloud Container
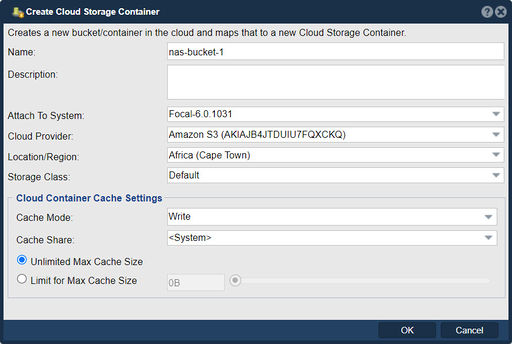
Create a Cloud Container using the 'Create Cloud Storage Container' Dialog. In the dialog, specify a name for the Cloud Container, the Cloud Provider, the Location for the Cloud Provider object storage you wish to use (public or private) , which of the systems in your grid you wish to attach to the Cloud Container and the Passphrase/Encryption Key to secure the object storage and click OK to create your Cloud Container.
Navigation: Cloud Integration --> Cloud Storage Containers --> Cloud Container --> Create (toolbar)
This is shown in the example:
Once the Cloud Container has been created, you can configure Network Share users and permissions via the Network Shares section of the Web interface: Managing Network Shares
Cloud Container Operations
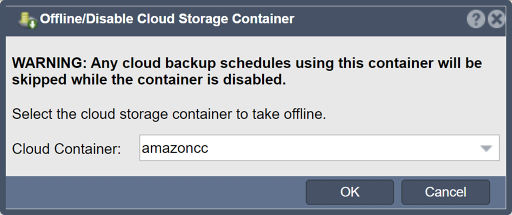
Offline/Disable access to a Cloud Container on a a QuantaStor System: Disable Cloud Container
Navigation: Cloud Integration --> Cloud Storage Containers --> Cloud Container --> Disable (toolbar)
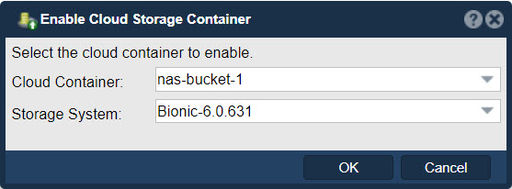
Enabling access to a offline Cloud Container on a a QuantaStor System: Enable Cloud Container
Navigation: Cloud Integration --> Cloud Storage Containers --> Cloud Container --> Enable (toolbar)
For additional information: Cloud Containers/NAS Gateway
Delete Cloud container: Delete the cloud container from the system. This will remove the cloud container from the system, but retain the bucket in the cloud. You can re-add the cloud container later using the 'Add Cloud Container' dialog. To permanently delete the bucket and its contents select "Delete bucket and contents from the cloud."
Importing existing Cloud Containers to a QuantaStor System: Import/Add Cloud Container
Permanently deleting a Cloud Container, it's objects and it's bucket in the Object Storage: Delete Cloud Container
Cloud Provider Support
QuantaStor has support for most major public cloud object storage vendors including Amazon AWS S3, IBM Cloud Object Storage (S3 & SWIFT), Microsoft Azure Blob and others. The sections below outline the configuration steps required to create authentication keys required to make an object storage "bucket" available as NAS storage within QuantaStor.
Amazon Cloud Storage Configuration Steps
Backblaze B2 Cloud Storage Configuration Steps
[Backblaze B2 Cloud Integration]